Textile sludge management
130 likes | 171 Vues
Presentation about 'Textile sludge management'

Textile sludge management
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Sludge is the solid material removed during the treatment of wastewaters. The term is also sometimes used as a general term for solids separated from suspension in a liquid material usually contains significant quantities of wastewater. There are three kinds of sludge: sewage sludge from municipal treatment works, septage pumped from septic tanks, and industrial smudges. All three are a growing management problem in this state, and throughout the world. A primary treatment plant removes solids physically, by screening out larger objects and allowing grit and other materials to settle in settling tanks. This removes most solids, but leaves suspended matter and dissolved substances in the discharged water, or effluent.
The Sludge management consist of different distinct functions such as Solid Liquid separation, Sludge Thickening, Sludge De- watering and Sludge disposal. The following Equipments manufactured by Confident play significant role in Sludge Management Process. High Rate Solid Content Clarifier Sludge Thickener Filter Press Hydro Extractor Decanter
Characteristics and aluminum reuse of textile sludge incineration residues after acidification The chemical composition and aluminum speciation of sludge incineration residue (SIR) were determined. Cementation of aluminum from sulfuric acid solution using SIR was studied. The results showed that acid- soluble inorganic aluminum was the predominant component in the sludge, and the total leached aluminum increased from 62.2% to 92.9% after incineration. Sulfuric acid dosage and reaction time were found to affect aluminum recovery positively. Conversely, the increase in temperature significantly inhibited recovery reactions. The optimized leaching condition was 1.66 g sulfuric acid per gram of SIR with a reaction time of 3 hr at 20°C, resulting in the highest aluminum leaching rate of 96.7%. Compared to commercial aluminum sulfate solution coagulants, the leaching solution demonstrated higher CODCr, turbidity and color removal efficiency for textile wastewater.
Brick manufactured from incinerated sewage sludge ash and clay is investigated. The results of Atterberg limits tests of molded ash-clay mixtures indicated that both plastic index and dry shrinkage decrease with an increasing amount of ash in the mixture. Results of tests indicated that the ash proportion and firing temperature were the two key factors determining the quality of brick. Increasing the firing temperature and decreasing the amount of ash in the brick resulted in a decrease of water absorption. The appropriate percentage of ash content for producing quality bricks was in the range of 20 to 40% by weight with a 13 to 15% optimum moisture content prepared in the molded mixture and firing at 1,000°C for 6 h. With 10% ash content, the ash-clay bricks exhibited higher compressive strength than normal clay bricks. This study showed that the pulverized sludge ash could be used as brick material. The bonding strength can be further enhanced by controlling operating conditions.
These regulations implement Council Directive 86/278/EEC on the protection of the environment, and in particular soil, when sewage sludge is used on agricultural land. They prohibit the use of sludge from sewage treatment works being spread on agricultural land unless specified requirements are fulfilled. The soil and the sludge must be tested before sludge is applied to land to determine the application rate, so as to avoid a build up of nutrients and heavy metals. The sludge producer must keep a register of the quality and quantities of sludge supplied for use in agriculture, the details of the person and farmland supplied and the analysis and assessments carried out on the farmland used. The occupier of the land must supply the producer of the sludge with information about the agricultural units on which the sludge was applied and how it was used. The Regulations also specify certain activities that are not permitted on land following sludge application, until certain periods of time have elapsed. Enforcement of this legislation is carried out by the Department of the Environment.
Commonplace requirements in many industries are to minimize the amount of waste generated and to reduce the overall impacts on the environment. Pulp and paper industries and automobile manufacturing unit generate a considerable amount of diverse hazardous waste. There are now standard practices or norms available for such industries. A number of methods are used for disposal of such kind of waste and reduce the concentrations of contaminants. The waste after conventional treatment results into sludge, ash or cake which contains residual contaminants mostly consisting of heavy metals / inorganic concentrates. These waste ends up in waste moulds or a landfill. In India, about 4.4 million tones/ annum of Hazardous Waste, which ends up for disposal. Unless this is scientifically disposed, it could cause serious hazard to human health. Why use a Hazardous Waste Landfill Low costs compared to other disposal options Often the only final disposal route for residues arising from other HWM options (e.g. ashes from incineration processes) Well-designed landfills can be unobtrusive
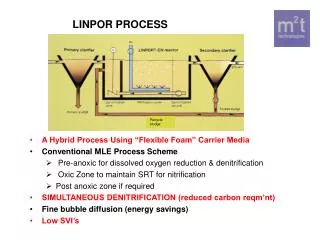
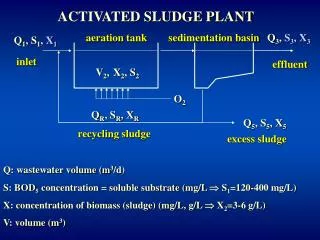
A Special Way to Manage Textile Sludge: Activated Sludge Process Process in which a mixture of wastewater and microorganisms is agitated and aerated Leads to oxidation of dissolved organics After oxidation, separate sludge from wastewater Induce microbial growth
Activated Sludge Process w/w Return Activated Sludge (RAS) Mixed Liquor in Reactor Air Treated w/w Secondary Clarifier Discharge to River or Land Application Waste Activated Sludge (WAS)
Please Ask any Question ?? Thank You All