Media and Soils
610 likes | 633 Vues
Learn about different types of growing media and soil particles, their roles in plant growth, soilless media, hydroponics, minerals, nutrients, soil texture, structure, and the importance of pH balance for healthy plants.

Media and Soils
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Media and Soils Chapter 6
Learning Targets • I can identify various types of growing media? • I can identify 3 Soil Particles.
Growing Medium • Material in which the roots plants grow.
Roles of Media • Provides nutrients and a anchor for plant.
Nutrients • Substance that roots absorb from the medium and water.
Anchor • Roots hold plant in place.
Pore Space • Air holes between the growing medium particles which allows oxygen to reach the roots of plants.
Soil Amendment • Anything added to the soil to improve plant growth. • Vermiculite • Perlite
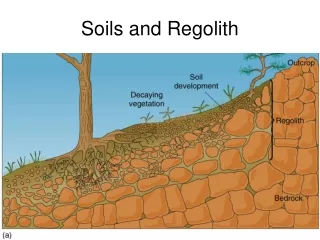
Soil • Top few inches of earths surface that provide soil growth.
Soilless Medium • Contains no soil. • Made from: • Vermiculite • Perlite • Peat Moss • Bark • Can be pre-mixed
Hydroponics • Nutrients are provided by nutrient solution.
Nutrient Solution • Contains water with dissolved nutrients.
Hydroponic Advantages • Nutrients Control • Yield is greater • Roots do not spread • Reduced Weed, Insect, Disease
Mineral Materials • Come from inorganic sources. • 3 kinds of Mineral Materials
Sand #1 • Largest material in soil. • Good for soil drainage.
Silt #2 • Smaller than sand. • Areas near rivers are high in silt.
Clay #3 • Smallest size particle in soil. • Holds water well. • Fills gaps between Sand and Silt
Organic Matter • Decayed remains from plants and animals.
Soil Texture • % of Sand, Silt, Clay present in the soil.
Soil Triangle • Used to classify soil on the basis texture content. • Most crops prefer a Loamy soil.
Loam Soil • High in Silt lower in Sand and Clay.
Soil Structure • Physical arrangement of soil particles.
Soil Aeration • Movement of air in the soil. • Clay soil least air movement.
Soil Compaction • Soil compressed into a dense mass.
Wear • Physical deterioration of a plant community.
Soil Profile • Vertical section of soil at a location.
Soil Horizon (A) • Topsoil: 10” Made of: • Humus • Roots • Organisms
Soil Horizon (B) • Subsoil: 30” • Made of: • Fine Particles • Leached materials • Some Roots
Soil Horizon (C) • Parent Material: 48” • Made of: • Bedrock • Leached materials
Soil Horizon (R) • Bedrock: • Made of: • Solid Rock
Plant Nutrients • 17 elements are needed for plants to grow.
Macronutrients • Most important nutrients needed in large amount.
Macronutrients • (N) – Nitrogen • (P) – Phosphorus • (K) – Potassium • (Ca) – Calcium • (Mg) – Magnesium • (S) – Sulfur
Primary Nutrients • N-P-K • Needed in largest amounts.
Secondary Nutrients • Ca-Mg-S • Needed in moderate amounts
Micronutrients • Needed in smaller amounts. • AKA-Trace Elements
Micronutrients • (Fe) – Iron • (Mn) – Maganese • (Zn) – Zinc • (Cu) – Copper • (B) – Boron • (Mo) – Molybdenum • (Cl) – Chlorine • (Ni) - Nickel
Soil Testing • Determines what nutrients are present in the soil.
Nitrogen • Key element • Helps plant recover from damage.
Nitrogen Deficient Example • Older leaves turn yellow. (Chlorosis) • Death can happen
Phosphorus • Helps plant hold and transfer energy for metabolism.
Phosphorus Deficient • Reduced growth • Dark to reddish leaf colorations.
Potassium • Important for plant life process.
Potassium Deficient • Reduced growth • Increase disease • Stress of plant
Soil PH • Ph is used to measure the amount of Alkalinity or acidity in soil.
PH Scale • 14 Point Scale
PH Scale • 7.0 = Neutral
PH Scale • Below 7.0 = Acidic • Above 7.0 = Alkaline
Modifying PH • Adding Lime will raise PH. • Adding Sulfur will lower PH.
Modifying PH • Most plants prefer PH of 5.5-8.0