Forestry
400 likes | 696 Vues
Forestry. But first….let’s talk trees!. The science of trees is dendrology. Boreal Forest - Quebec. Forests are important in cities as well. Peterborough, ON. Classification Systems Leaf Type – broad leaves vs. needles

Forestry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
But first….let’s talk trees! • The science of trees is dendrology.
Forests are important in cities as well. Peterborough, ON
Classification Systems • Leaf Type – broad leaves vs. needles • Deciduous – lose leaves at one timeEvergreen – lose leaves or needles and gradually replace them
Conifers (gymosperms) – seeds are contained in cones (softwoods) • Flowering Trees (angiosperms) – seeds are hidden inside fruit (hardwoods)
History of Forestry • Thousands of years ago, much of Europe was covered in forests • The Middle Ages saw significant deforestation as human population increased.
Original Forest Cover 2005 Forest Cover Europe has lost about 99% of its original forest
North America • Early 1600s – lumber was essential to the economy (East Coast Maine was the world’s largest shipping port for lumber) • Lumber was used to build ships • Extraction of lumber increased dramatically during the Industrial Revolution
Canada – some statistics • Canada has 10% of the world’s forests • Forests cover nearly ½ the country • 180 tree species in Canada • 94% is publically owned (government or “crown land”) 6% privately • Also urban forests (parkland in cities) • 300,000 jobs, 300 forestry based communities • $30 billion dollar industry (exports) • Newsprint, paper, lumber, woodpulp
Three Major Types of Forest • Old-Growth Forest – has never been harvested or seriously disturbed by human activities or natural disasters for several hundred years • Second-Growth Forest – develop naturally after trees in an area have been harvested or removed • Tree Plantations - or tree farms – managed area of same-age trees of one species
Silviculture • Silviculture is a system of controlling the planting, growth, composition, health, and quality of forests to meet diverse needs and values of the many landowners, societies and cultures. • In other words, silvicuture is the growing, tending, and harvesting of trees instead of field crops
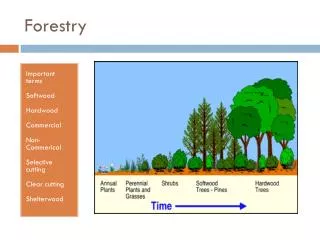
Three basic systems (handout) • Clearcutting • Selective Cutting • Shelterwood • There are advantages and disadvantages for each
Forests are a renewable resource • Unlike fossil fuels or mined metals, the practice of harvesting trees CAN be sustainable, when trees are replaced at the rate they are harvested. • In Canada, forest companies are required to replant after they log.
Environmental Effects of Forestry • Climate Change – reduction of a natural sink for CO2 (less photosynthesis) • Reduction of biodiversity • Habitat loss • Soil Erosion (vegetation removal) • Monoculture (reforestation) can make forests more susceptible to disease and pests • Reforested areas – less undergrowth and decaying material so less habitat for animals