Forestry
340 likes | 506 Vues
This overview explores various forestry practices in Pennsylvania, including cut types like selection, selective, shelterwood, and clear-cutting, along with their ecological impacts. It highlights how these methods influence forest structure, water management, and biodiversity. The significance of forests to Pennsylvania’s economy, which covers 30% of the landscape with 17 million acres, is discussed alongside the importance of maintaining wildlife habitats and addressing forestry problems such as road erosion and invasive species.

Forestry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tree terms Saw log- 6-8 inches for soft wood, 10-12 inches for hardwoods
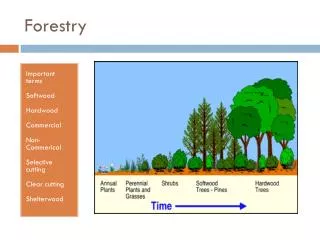
More Cut Types • Selection cut- promotes uneven aged stands • Selective cut- removes oldest, most valuable trees, bad for forest growth • Shelterwood retains 30-70% of canopy • Clear cutting is good for PA forests because it allows sun loving trees like black cherry and oak to regenerate
Fires • 98% ignited by humans, mostly burning debris
PA Forestry • 30% of PA economy is based on forestry • 17 million Acres of forest cover, almost 60 % of the State • Produces more than a billion board feet of hardwood and three-quarters of a million cords of pulpwood • Most of PA white pine & hemlock forests cut by early 1900s • Now even aged mixed hardwoods • 90% of PA trees are hardwoods
Forest Affect on Water • Incepts & infiltrates water • Trees Consume Storm Water • Removes Pollutants • Phytoremediation – examples trees in parking lots • Riparian Buffers
Forestry Problems • Skidding is the process of dragging logs from the stumps to a central location, called a log landing, where they are loaded onto trucks and transported to the mill. • Log landings create large areas of unprotected, exposed soil • Roads disturb soil, increase erosion • Sewage removal • Pesticide use
More facts • Trees are plants that can reach at least 15 ft tall • Forest is land with at least 10% trees
Forest Fragmentation • Increases spread of invasives • Decreases mobility and habitat size of natives
Mixed-oak forests • Contain primarily the oaks; including northern red oak, chestnut oak, white oak, scarlet oak; along with the maples, yellow-poplar, ash, hickories, and miscellaneous deciduous species. • The understory vegetation is mountain laurel and blueberry.
Northern hardwood forests • Contain primarily black cherry, the maples, American beech, the birches • Understory composition often comprised of ferns, striped maple and beech brush. • Hemlock and eastern white pine are common to both forest types and both produce valuable wood products
Forest Types • Forest Openings- herbaceous rather than woody growth; insects, small mammals • Brush stage- small, dense, woody vegetation; browse and fruit, nesting cover • Pole timber- less wildlife value, more timber value • Mast/Mature timber- (mast is the fruit of woody plants) high protein and fat for animals,
Tree Types • Large old- nesting cavities, roosting, mast • Snags and cavity- dead but standing, perches, cavities • Evergreens- cover from cold and snow • Vines, shrubs, fruit- form understory • Riparian- form fish and wildlife habitats, act as sponges
Special Habitats • Wetlands- most productive, but least common in PA; greatest biodiversity • Seep Springs- Snow free in winter, providing water and food • Cliffs- secure nesting and unique habitats • Caves- shelter, nesting, and roosting
Factors the Increase Extinction • Specializers • Sought by People • Rare • Codependent • Top of the Food Chain • Low Reproduction Rate