Respiratory System
380 likes | 509 Vues
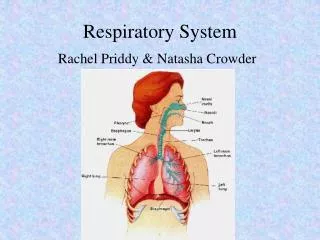
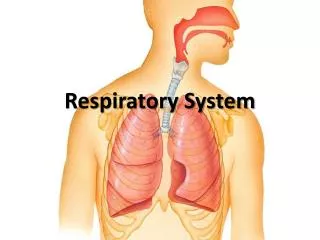
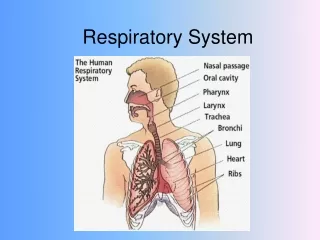
The respiratory system, primarily consisting of the lungs and air passages, plays a crucial role in breathing by taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. This system includes various components: the nasal passages warm and filter air, the pharynx aids in swallowing, and the larynx produces sound. The trachea and bronchi direct air to the lungs, where alveoli facilitate gas exchange. The diaphragm assists in ventilation, controlled by the brain. Understanding common diseases like asthma, bronchitis, and pneumonia is vital for respiratory health.

Respiratory System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Parts • Lungs • Air passages
Functions • Takes in oxygen • Removes carbon dioxide • Body has 4-6 minute supply of oxygen
Air PassagesNose • 2 nostrils or nares • Nasal septum • Divides nose into 2 nasal cavities • Lined • With mucous membrane with a rich blood supply • Functions • Warms • Moistens • Filters
Cilia • Tiny hair-like structures that help move dirt trapped in mucous to the esophagus • Olfactory Receptor • Receptors for sense of smell • Lacrimal Ducts • Tear ducts • Drain tears from the eye into the nose
Sinuses • Cavities in the skull that surround the nasal area • Connected to nasal cavities by short ducts • Function • Warms and moistens air • Lined with mucous membrane • Provides resonance for the voice
Pharynx • Throat • Lies behind the nasal passages • 3 sections • Nasopharynx • Oropharynx • Laryngopharynx
Larynx • Voice box • Layers of cartilage • Largest is the thyroid cartilage commonly called the Adam's apple • Contains • Vocal chords • Vibrate on exhaled air to produce sound • The tongue and lips act on the sound to produce speech • Epiglottis • Flap of cartilage that closes the larynx during swallowing and prevents food and liquids from entering the trachea
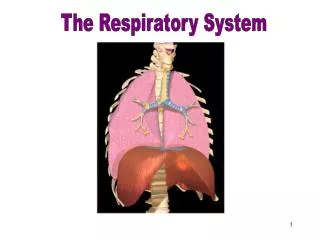
Trachea • Windpipe • Series of “C” shaped cartilage to keep the tube open to the back • Divide into the right and left bronchi • Continues to divide into smaller bronchioles • End in the alveoli • Air sacs
Alveoli • One cell thick and surrounded by capillaries • Look like a cluster of grapes • Allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Surfactant • Surfactant • Reduces surface pressure and prevents alveoli from collapsing
Lungs • Right lung 3 lobes • Left lung 2 lobes due to the heart
Pleura • Covered by a double layer sac called the pleura
Ventilation • Process of breathing • Diaphragm • Muscle of respiration • Assisted by the intercostal muscles • Phases of respiration • Inspiration • Inhale • Expiration • Exhale
Diaphragm Dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
Process of Respiration • Controlled by the medulla oblongata in the brain • An increase in amount of CO2 in the blood , increases the rate of respiration • Both involuntary and voluntary process
Stages of Respiration • External Respiration • Exchange of gases between air in the lung and the blood
Internal Respiration • Exchange of gases between the blood and the cells
Cellular Respiration • Use of gases to make energy, water and CO2
Diseases • Asthma • Inflammation of airways with increased mucous production and muscle constriction • Cause – allergen, exercise, stress, chemical • S/S - wheezing, coughing, dyspnea, shortness of breath • Tx - bronchodilators, steroids
Bronchitis • Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchial tubes • Acute – infection • Chronic – longtime exposure to smoking • S/S productive cough, dyspnea, fever, chest pain • Tx – antibiotics, bronchodilators, oxygen
Emphysema • Non infectious, chronic respiratory condition when walls of alveoli deteriorate and loss elasticity • CO2 remains trapped in the alveoli • Poor exchange of gases • S/S dypnea, feeling of suffocation, barrel chest • TX – No cure
Epistaxis • Nosebleed • Congested capillaries bleed • Due to injury, blowing too hard, hypertension • TX – pinch nostrils lean forward slightly
Influenza • Flu • Viral infection of the lungs • Spread by respiratory droplet • S/S - fever, malaise, chills, cough, sore throat, muscle pain • Tx - symptomatic
Lung Cancer • Leading cause of death of men and women • S/S no symptoms in early stages, later cough hemoptysis • Tx – surgical removal, radiation, chemotherapy
Pneumonia • Inflammation or infection of the lungs • Build up of exudates (fluid) in the alveoli • S/S cough, chest pain, fever, dyspnea • Tx – antibiotics, bed rest, fluids, respiratory therapy, pain medication
Tuberculosis • Infectious lung disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Can be walled off in a tubercle and become dormant • New strains are drug resistant • S/S fatigue, fever, night sweats, hemoptysis weight loss, chest pain • Tx - several drugs over a period of two years