Understanding Acids and Bases: Properties, Nomenclature, and pH Scale
70 likes | 190 Vues
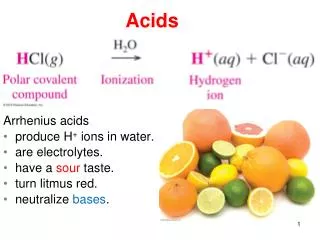
Acids and bases are fundamental chemistry concepts with distinct properties. Acids are sour, conduct electricity in aqueous solutions, turn litmus paper red, and can neutralize bases. Common binary acids like hydrofluoric (HF) and hydrochloric (HCl) follow specific nomenclature rules. Meanwhile, oxyacids, such as acetic acid (HC2H3O2) derived from acetate, offer additional examples. On the other hand, bases are typically metal hydroxides that turn litmus paper blue. Understanding the pH scale is crucial: lower pH indicates acidity, while higher pH signifies basicity, with 7 as neutral.

Understanding Acids and Bases: Properties, Nomenclature, and pH Scale
E N D
Presentation Transcript
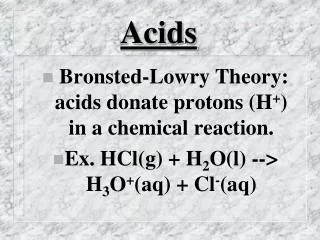
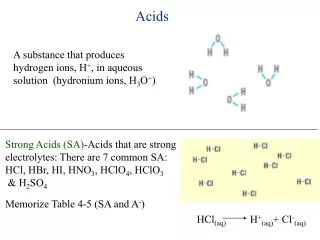
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity, tastes sour, turns litmus paper red, and neutralizes bases Acids
NomenclatureCommon Binary Acids: hydro- Cross over rule: • Hydrofluoric acid HF (aq) • Hydrochloric acid HCl (aq) • Hydrobromic acid HBr (aq) • Hydrosulfuric acid H2S (aq)
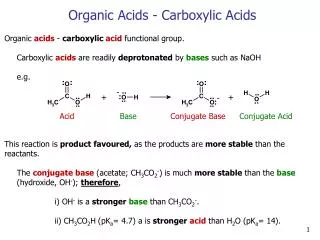
Common Oxyacids (Polyatomic) • Acetic acid HC2H3O2 (aq) comes from acetate C2H3O2 – • Phosphoric acid (aq) comes from phosphate PO43-
Try these: • Carbonic acid • Sulfuric acid
Bases • An aqueous solution that conducts electricity and turns litmus paper blue • Usually a base is a metal and hydroxide • Cross over rule applies: • Sodium hydroxide is: • Calcium hydroxide is: • Magnesium hydroxide is: • Aluminum hydroxide is: • Ammonium hydroxide is:
Power of Hydrogen: pH scalea very acidic solution has a low pH numbera very basic solution has a high pH numbera neutral substance has a pH of 7 (in the middle)
Homework • P. 271 # 1-5 • P. 275 # 2-4