Understanding Stellar Evolution: The Lifecycle of Stars
150 likes | 298 Vues
This introduction to stellar evolution explores the life stages of stars, from their formation in molecular clouds to their eventual demise. It presents the processes of protostar formation, main sequence stability, and various end-of-life outcomes including white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. Additionally, it explains fusion processes such as the proton-proton chain and the CNO cycle, highlighting differences between low-mass, mid-sized, and massive stars. This educational resource is essential for anyone interested in the cosmos and the life cycles that govern our universe.

Understanding Stellar Evolution: The Lifecycle of Stars
E N D
Presentation Transcript
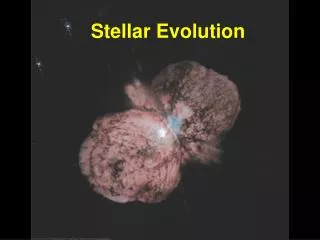
A Brief Introduction to Stellar Evolution Teatime No.44 FAS, 2009
A star • What is a star?
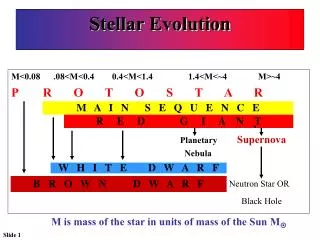
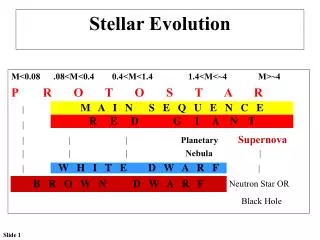
Lifetime of a star • Molecular cloud • Protostar • Star • End of a star
Molecular cloud • H2 • Gravity • Collapse
Protostar • Duration: 10^5 a (1 solar mass) • Cluster • Heating • End of protostar • Brown dwarf • star
Star • Main sequence • Fusion • PP Chain • CNO cycle • duration • Next…
Next… • Low-mass (~0.4 M⊙) • May stay for trillions of a, longer then recent life of universe • End in a white dwarf • theoretically • Mid-sized • Massive
Next… • Low-mass • Mid-sized (0.4 M⊙~2.25 M⊙ ~9 M⊙) • Helium fusion(3 α process) • Red Giant • Life: 10 billion a • Sun • Massive
Next… • Low-mass • Mid-sized • Massive (9 M⊙~above) • Fusion ends at Fe-56 • Red Giant/ Red Super Giant • Supernova • Life time: ~ 1 million a • Neutron star/ Black hole
End • White Dwarf • Neutron star • Black Hole
acknowledgement • 大众天文学 C. 弗拉马里翁 • 香港大学物理系宇宙的本质讲义 • http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/EducationResource/Universe/framed_c/index.html • http://zh.wikipedia.org/内的相关条目