Understanding Magnetism: Concepts, Fields, and Forces
250 likes | 369 Vues
This comprehensive overview of magnetism explores what magnets are, their properties, and the fundamental principles governing magnetic fields. Learn about the two poles of magnets—north and south—and the law of poles, which states that like poles repel while opposite poles attract. Delve into Earth's magnetic field, the role of electric currents in generating magnetic fields, and the interaction between magnetism and electricity. This guide includes key concepts such as magnetic fields in solenoids, the right-hand rule, and electromagnetic induction.

Understanding Magnetism: Concepts, Fields, and Forces
E N D
Presentation Transcript
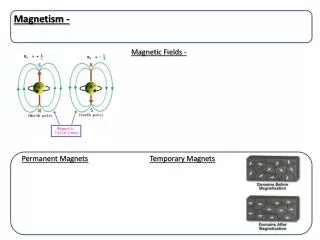
What is a magnet? • An object that attracts iron containing objects • Has two poles • North and south • Law of poles- • Like poles repel while opposite attract
Clicker Question • A bar magnet is divided into two pieces. Which of the following statements is true? • A) the bar magnet is demagnetized • B) the magnetic field of each separated piece becomes stronger • C)the magnetic poles are separated • D) two new bar magnets are created
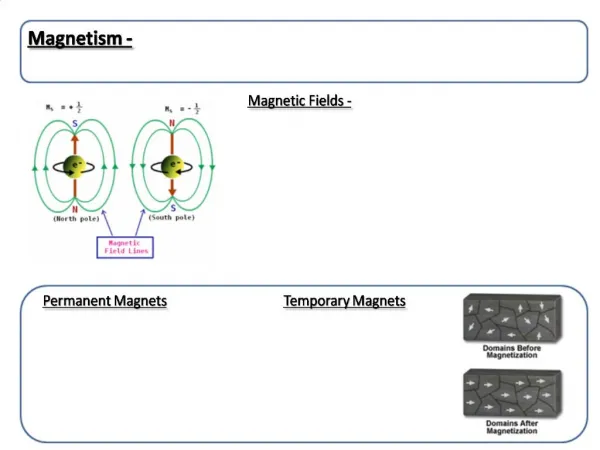
What are magnetic fields? • A region in which the magnetic force can be detected • The magnetic fields go from the north pole to the south pole
Clicker Question • Magnetic Field Diagram # 3
Magnetic Field Lines • Also called flux lines • Never cross each other • The closer they are the stronger the field
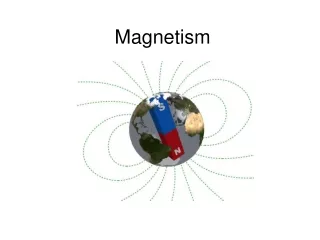
Earth’s Magnetic Field • ???
Earth’s Magnetic Field • The north pole is actually the south pole of Earth’s magnet! • The magnetic south pole is near the geographic North pole and vice versa. • This is why compasses point to the south pole of a magnet in a magnetic field but we say that compasses point north
Clicker Question Which of the following statements is most correct? A.The north pole of a freely rotating magnet points north because the magnetic pole near the geographic North Pole is like the north pole of a magnet. B.The north pole of a freely rotating magnet points north because the magnetic pole near the geographic North Pole is like the south pole of a magnet. C.The north pole of a freely rotating magnet points south because the magnetic pole near the geographic South Pole is like the north pole of a magnet. D. The north pole of a freely rotating magnet points south because the magnetic pole near the geographic South Pole is like the south pole of a magnet.
What is magnetism caused by • Caused by moving charges • Any time a charge moves (current) a magnetic field is created • So….electric current can create magnetic fields • Magnetic force is created by two magnetic fields occupying the same space
What are magnets? • Electrons have a spin, so there are moving charges in atoms • Most atoms’ electrons are paired up though and spinning in opposite directions, so the fields that are generated are cancelled • When the electrons are not paired up then the fields are not cancelled • These materials can be magnetic
Electric Fields Versus Magnetic Fields • Electric Fields • Caused from a positive or negative charges • Charges can be moving or stationary • Fields move from positive to negative • Can be caused by a single charge • Magnetic Fields • Caused from moving charges • Field lines move from north to south pole • Always caused from two poles
Magnetic Fields and Current • When there is an electric current a magnetic field (B-field) is created around it • Use the right hand rule • Thumb will point in the direction of the current • Fingers will curl in the direction of the B field
Clicker Question • An electric current flows into the page. What is the direction of the magnetic field? • A) to the bottom of the page • B)to the top of the page • C)Clockwise • D)counter-clockwise • E) to the right
Clicker Question • A current is flowing to the right, in what direction will the magnetic field be? • A)Into the page • B)out of the page • C)clockwise • D)counter-clockwise • E)to the left
Magnetic Fields in Solenoids • Solenoid is a long helically wound coil of wire • Solenoids produce a strong magnetic field by combining several loops • More loops= stronger magnetic field
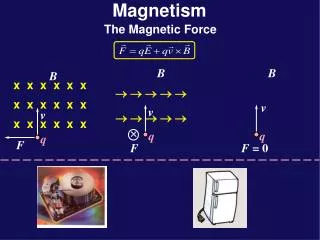
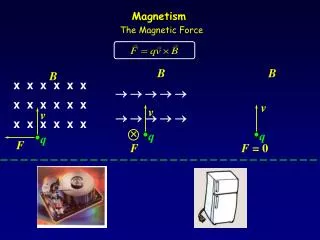
Magnetic Force • A charge moving through a magnetic field experiences a magnetic force • The force is proportional to the • Charge • Velocity • Magnetic field
Magnetic Force • Alternative Right Hand Rule • Direction of your palm=magnetic force • Fingers= magnetic field lines • Thumb=velocity of particle • When drawing • An X= into the page • A = out of the page
Clicker Question • A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. What is the direction of the magnetic force? Velocity is pointed up and fields pointed into page. • A) out of the page • B) into the page • C) downwards • D) to the right • E) to the left
Clicker Question • A positive charge enters a uniform magnetic field. What is the direction of the magnetic force? The velocity is to the right and the magnetic field is into the page. • A) out of the page • B) into the page • C) Downwards • D) upwards • E) to the left
Multiple Wires • If two wires were parallel to each other and the current was in the same direction, they would attract • If the current is in the opposite direction they would repel
Electromagnetic Induction • Changing magnetic fields creates a potential difference (or EMF) in a conductor • So.. Magnetic fields can create currents • This allows physical work to create electrical energy
Transformers • Power that is generated for transmission (for homes and buildings) is ramped up (about 100000 V) when it arrives at your home you need it at a lower level (120V) • To convert voltage to a higher or lower value we use a transformer
Transformer • Consists of a primary coil and a secondary coil • The current flows through the primary magnetic field • Magnetic field current in secondary coil • We use alternating current for this • When a transformer increases voltage it is called a step up (more secondary coils) • When a transformer decrease voltage it is called a step down (more primary coils)