Understanding Brain Hemispheric Differences: Language and Spatial Abilities Explained
200 likes | 363 Vues
This module explores the intricacies of brain hemispheric differences, debunking the common myths of "left-brained" and "right-brained" individuals. It details the roles of both hemispheres, highlighting that they operate as a unified entity, constantly communicating via the corpus callosum. Key areas like Broca's and Wernicke's in the left hemisphere are essential for language, whereas the right hemisphere manages spatial abilities. The module also touches on brain plasticity and its significance, especially in cases of brain damage and split-brain conditions.

Understanding Brain Hemispheric Differences: Language and Spatial Abilities Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hemispheric Differences Module 8: The Brain
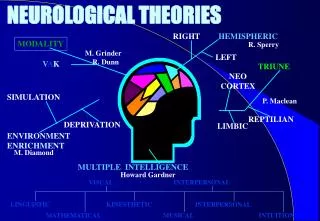
Hemispheric Differences • “Left-brained” and “right-brained” debunked • Brain is divided into two hemispheres but works as a single entity. • Both sides continually communicate via the corpus callosum, except in those with split brains.
Hemispheric Differences: Language and Spatial Abilities Module 8: The Brain
The Brain’s Left Hemisphere • For most people, language functions are in the left hemisphere. • For a small percentage of people, language functions are in the right hemisphere.
Broca’s Area • Located in the frontal lobe and usually in the left hemisphere • Responsible for the muscle movements of speech • If damaged the person can form the ideas but cannot express them as speech (stroke victims)
Wernicke’s Area • Located in the temporal lobe • Involved in language comprehension and expression; our ability to understand what is said to us • Usually in the left temporal lobe
The Brain’s Right Hemisphere • Houses the brain’s spatial abilities • Our spatial ability allows us to perceive or organize things in a given space, judge distance, etc. • Helps in making connections between words
Brain Plasticity Module 8: The Brain
Plasticity • The ability of the brain tissue to take on new functions • Greatest in childhood • Important if parts of the brain are damaged or destroyed
Split brain patients • Video • Cut corpse callosum
hemispherectomy • Video – united streaming
Name of Concept • Use this slide to add a concept to the presentation
Name of Concept Use this slide to add a table, chart, clip art, picture, diagram, or video clip. Delete this box when finished