Argument vs. Assertion
50 likes | 165 Vues
Learn about the distinctions between arguments and assertions, including definitions, characteristics, and examples. Explore how arguments involve reasoning with evidence, while assertions may lack logical support. By examining these concepts, you can enhance your critical thinking skills and communication abilities.

Argument vs. Assertion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
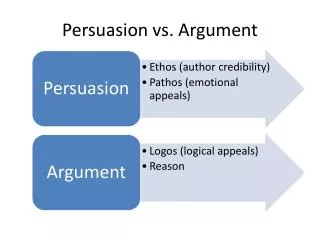
Assertion • A judgment or conclusion that is presented by itself without reasons to support it • EX: Mr. Jones is a horrible teacher. • Made to seem as though idea is an accepted fact • Often results from subjective reasoning • A conclusion obtained from reasons an individual believes to be true • Individual accepts the conclusion, he asserts it as fact
Assertion Con’t • Labeling (name-calling) • Occur in emotionally charged situations • Not dominated by logical reasoning • Considered a type of assertion • Innuendo • An assertion that is not directly stated, but implied or hinted at
Argument • Conversation that contains at least two statements • Includes one reason and one conclusion • Some arguments contain 3 parts: • 1. reason (evidence) • 2. signpost word/transition • Therefore, hence, accordingly, as a result, so, consequently, thus, because, since, as indicated by… • 3. conclusion
Argument Example Exercise stimulates the brain, releases endorphins, and heightens awareness; therefore, athletes are better students than others. Reason Signpost word Conclusion