Ligand Docking to MHC Class I Molecules
120 likes | 404 Vues
Ligand Docking to MHC Class I Molecules . Lam Tze Hau. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I. Play a vital role in the adaptive immune response. Generate maximal immunological protection against a large repertoire of pathogens.

Ligand Docking to MHC Class I Molecules
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ligand Docking to MHC Class I Molecules Lam Tze Hau
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I • Play a vital role in the adaptive immune response. • Generate maximal immunological protection against a large repertoire of pathogens. • MHC bind to peptides of diverse sequences degraded from pathogen proteins and present on cells surface for T-cell recognition to initial and regulates immune responses Tobias Jung et al, 2009
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I • MHC class I molecules are highly polymorphic. • 3 major human MHC genes commonly referred as HLA (A, B, C). • More than 1000 of HLA class I alleles are known. • Strong bias for stable binding of short peptides in the range of 8 – 10 residues. • Peptide binding specificity to MHC is allele specific.
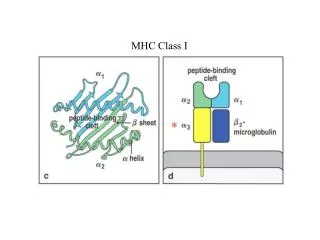
Structure of class I MHC-peptide complex • Binding clefts contain polymorphic ‘pockets’ that fits the complementary residues of the binding peptides. • H-bonds between the peptide termini and the conserved MHC residues anchor the N- and C- termini. • Backbone conformation of the 3 N-terminal peptide residues and the 2 C-terminal residues is similar in many different MHC-pepitdes structures. • These positions contribute most of the binding interactions. • Specific MHC alleles bind peptides with similar anchor residues.
MHC class I peptides prediction • The understanding of the peptide selection and interactions for different MHC alleles is important. • It is crucial step for establishing T-cell-based immunotherapy for infectious diseases , autoimmune diseases and cancer. • Experimental studies are time-consuming and expensive. • In silicoapproaches: • Sequence-based • Structure-based
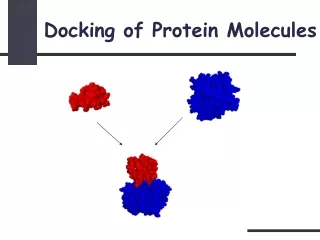
Structure based approach-Molecular Docking • Useful technique to study intermolecular interactions or structure based drug design. • Motivation of docking simulation • To determine the most probable translational, rotational and conformational position of a given ligand-receptor. • To evaluate the relative goodness-of-fit for different computed complexes. • Docking simulation is highly combinatorial in nature. • Search on the conformation space increases exponentially with increase molecule size and sampling space.
Molecular Docking - AutoDock • AutoDock is a suite of automated docking tools. • Consist of 2 main programs: • AutoGrid pre-calculates these grids. • AutoDock performs the docking of the ligand to a set of grids describing the target protein
Molecular Docking - AutoDock • AutoDock uses semi empirical free energy force field to evaluate conformations during docking simulation. • Allows configurations for flexible ligand and receptor side chains. Garrett M. Morris et al , 2010
Molecular Docking - AutoDock • AutoDock molecular simulation of a peptide (9mer) onto MHC binding cleft requires approx ~ 4 to 6 hours. (50 conformations run with using Lamarckian genetic algorithm as the search method). • Docking thousands of potential pathogen peptides against hundreds of MHC class I molecules requires enormous amount of computational power.