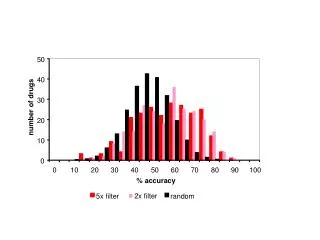
100
650 likes | 871 Vues
Phsyics Jeopardy. Work & Energy. v & a. Newton’s First. Newton’s Second. Newton’s Third. F D t = m D v. 100. 100. 100. 100. 100. 100. 200. 200. 200. 200. 200. 200. 300. 300. 300. 300. 300. 300. 400. 400. 400. 400. 400. 400. 500. 500. 500. 500. 500. 500.

100
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Phsyics Jeopardy Work & Energy v & a Newton’s First Newton’s Second Newton’s Third FDt=mDv 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500
Distance is covered A 100
You walk across the room at 2 kilometers per hour. Show this as an abbreviated unit. A 200
km/h A 200
Velocity changes A 300
What is the acceleration of a vehicle that travels in a straight line at 100km/h? A 400
0 km/h2 A 400
Calculate the instantaneous speed and distance fallen for an object that falls freely from rest for 8 seconds. A 500
v=80m/s, d=320m A 500
If you were in a spaceship and fired a cannonball into frictionless space, how much force would have to be exerted on the ball to keep it going? B 100
(2kg)(9.8m/s2)=~20N B 200
Forces of 10N and 15N are pushing an object in the same direction. What is the net force? B 300
25N B 300
If forces of 10N and 15N push an object in opposite directions, what is the net force? B 400
+5N B 400
Susie Small finds that she weighs 300N. Calculate her mass. B 500
(300N)/(9.8m/s2)=~30kg B 500
How much force does a 20,000kg rocket develop to accelerate 1m/s2? C 100
(20000kg)(1m/s2)=20,000N C 100
If the force of friction on a sliding crate is 100N, how much force must be applied to maintain a constant velocity? C 200
100N C 200
Which has more pressure on the ground, a person standing up or a person lying down? C 300
Standing C 300
DAILY DOUBLE DAILY DOUBLE Place A Wager C 400
Calculate the acceleration of a 2000kg airplane just before takeoff when the thrust of its engine is 500N. C 400
(500N)/(2000kg)=0.25m/s2 C 400
Calculate the horizontal force that must be applied to produce an acceleration of 1.8g for a 1.2kg puck on a horizontal, friction-free table. C 500
When a hammer exerts a 20N force on a nail, how does the amount of force compare with that of the nail on the hammer? D 100
20N (same) D 100
Why can’t you it a feather in mid-air with a force of 200N? D 200
When you jump up, the Earth “jumps” down. Why don’t we notice this? D 400
How can a rocket be propelled above the atmosphere where there is no air to push against? D 500
The rocket is propelled by the reaction force of the gas D 500
Mass- inertia Momentum- inertia in motion E 100
Impact- force Impulse- force applied over time E 200
In terms of the impulse-momentum theorem, why is it advantageous to wear a seatbelt and have airbags? E 300
They extend the Dt of collision, thereby decreasing the force E 300
What is the momentum of an 8kg bowling ball rolling at 2m/s? E 400
(8kg)(2m/s)=16kg•m/s E 400