Parts of an Experiment
130 likes | 659 Vues
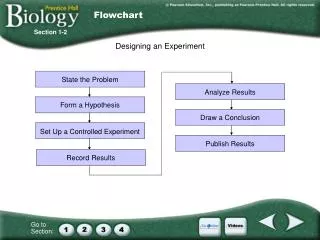
Parts of an Experiment. EXPERIMENT. Organized procedure for testing a hypothesis When designing an experiment there are certain things that you will need to include for it to be valid. Most experiments will need:. Control Group - “ standard of comparison ” Closest to actual conditions

Parts of an Experiment
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EXPERIMENT • Organized procedure for testing a hypothesis • When designing an experiment there are certain things that you will need to include for it to be valid.
Most experiments will need: • Control Group - “standard of comparison” Closest to actual conditions • Experimental Group - Differs from the control group by one factor or condition (which is called a…)
VARIABLE • The condition that makes the experimental group different from the control group. • You will want your experiment to have only one variable in it for the experiment to be valid.
Example: • Can plants grow without light? • What would be my control group? • What would be my experimental group? • What would my one variable be? • There are two types of variables to be familiar with…
Independent Variable • A factor that the experimenter has full control over and changes to see what happens • The “CAUSE”
Dependent Variable • A factor that changes because of what the experimenter does • The “EFFECT”
What about the things that need to be the same in both the control group and the experimental group?These things are called...
CONSTANTS • A factor that does not vary in an experiment • (It is the same in the control group as in the experimental group)