Genetics The study of heredity
380 likes | 693 Vues
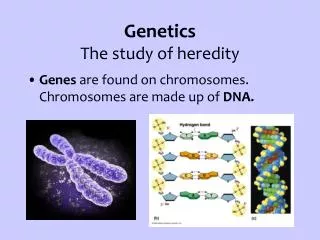
Genetics The study of heredity. Genes are found on chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of DNA. Alleles : Different forms of a gene. Dominant : If the dominant allele (gene) is present, the organism will show that trait.

Genetics The study of heredity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GeneticsThe study of heredity • Genes are found on chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of DNA.
Alleles: Different forms of a gene. Dominant: If the dominant allele (gene) is present, the organism will show that trait. Recessive: Trait will be exhibited only if organism does not have dominant allele or is pure for recessive trait.
Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)An Austrian monk who cultivated and studied garden pea plants. His studies produced the basic concepts of heredity.
Genotype: The Allele combination, heterozygous (hybrid) or homozygous (gg, GG, or Gg).Phenotype: The physical characteristic displayed (green or yellow).
Why Pea Plants? • Many observable contrasting • traits. • Easy to grow. • Short time between one • generation and the next.
Punnett SquareIn Pea plants Green pods (G) are dominant over yellow (g) pods. GenotypePhenotype GG homozygous Green Pod Gg heterozygous Green Pod gg Yellow Pod P Cross : GG x gg Possible Gametes : ____ ____ X ____ ____ g g F1 Genotypic ratio: F1 Phenotypic ratio: G G
F1 Cross: Gg x Gg Possible Gametes: ____ ____ X ____ ____ F2 Genotypic ratio: F2 Phenotypic ratio:
In mice black is dominant over white; B – black, b- white, BB homozygous black, Bb heterozygous black, bb recessive whiteCross two heterozygous black mice, Bb x Bb Cross : Bb x Bb Possible Gametes : ____ ____ X ____ ____ Genotypic ratio: Phenotypic ratio:
Test Cross Is this back mouse homozygous black BB or heterozygous black Bb? One way to find out is to do a Test Cross. Cross this black mouse with the recessive white bb. BB x bb Bb x bb If any of the offspring produced are white or show the recessive trait, then the black mouse had to be heterozygous Bb. If all of the offspring produced are black, you cannot be 100% positive that the black mouse is homozygous BB because the inheritance of a an allele is a 50/50 chance.
Dihybrid Cross 2 traits; plant height and seed color P Cross: TTRR ( pure tall & round) x ttrr (pure short & wrikled) _____ _____ ______ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
F1 Cross TtRr (hybrid tall & round) x TtRr (hybrid tall & round) _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____
Incomplete Dominance Genotype Phenotype RR Red flower WW White flower RW Pink flower P Cross: RR x WW W W F1 Genotype: 100% RW F1 Phenotype: 100% Pink flower R R
Co dominance Genotype Phenotype RR Red cow WW White cow RW Roan cow P Cross: RR x WW W W R R Genotype of F1 offspring: 100% RW Phenotype of F1 offspring: 100% Roan
Multiple AllelesBlood Types AlleleAntigen on RBC IA A IB B i none GenotypePhenotype IA IA homozygous Type A IA i heterozygous Type A IB IB homozygous Type B IB i heterozygous Type B IA IB Type AB i i Type O
Crosses Involving Multiple Alleles Cross: a man who is heterozygous for blood type A with a woman who is blood type O. IA i x i i Cross: a man who is homozygous for blood type A with a woman who is homozygous blood type B. IA IA x IB IB IB IB i i IA i IA IA
Sex Linked TraitsTraits located on the X chromosome GenotypePhenotype XX Normal Female XcX Carrier Female XcXc Colorblind Female XY Normal Male XcY Colorblind Male Cross: A normal male with a carrier female. XY x XcX Cross: A colorblind male with a carrier female. XcY x XcX Xc Y X Y Xc X Xc X
Karyotype Female XX Male XY