Chapter 13 Alkanes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds
690 likes | 1.41k Vues
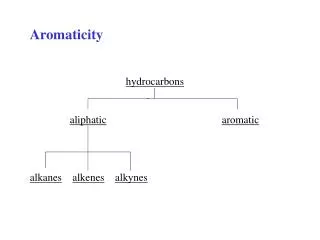
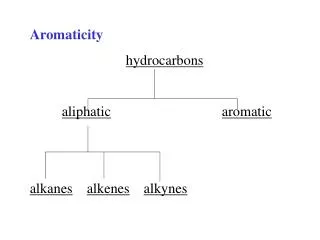
Chapter 13 Alkanes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds. Saturated Hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbons: Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Are alkanes and cycloalkanes with single C-C bonds. CH 3 —CH 2 —CH 3. 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes.

Chapter 13 Alkanes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Saturated Hydrocarbons Saturated hydrocarbons: • Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. • Are alkanes and cycloalkanes with single C-C bonds. CH3—CH2—CH3
13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes • Unsaturated hydrocarbons: • Have fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than alkanes. • Are alkenes with double bonds or alkynes with triple bonds.
Alkenes Have Double Bonds In a double bond: • One pair of electrons form a strong sigma () bond. • One pair of electrons in adjacent p orbitals overlap to form a pi () bond.
Alkynes have Triple Bonds In a triple bond: • One pair of electrons form a strong sigma () bond. • Two pairs of electrons in adjacent p orbitals overlap to form two pi () bonds.
Bond Angles in Alkenes and Alkynes According to VSEPR theory: • The three groups bonded to carbon atoms in a double bond are at angles of 120°. • The two groups bonded to each carbon in a triple bond are at angles of 180°.
13.2 Naming Alkenes and Alkynes • In the IUPAC system, the –ane ending of the corresponding alkane is changed to –ene for alkenes and to –ynefor alkynes.
Naming Alkenes and Alkynes When the carbon chain has 4 or more C atoms, the chain is numbered to give the lowest number to the double or triple bond. 1 CH2=CH—CH2—CH31-butene 2 CH3—CH=CH—CH2—CH32-pentene 3 CH3—CH2—CC—CH2—CH33 -hexyne
Learning Check Write the IUPAC name for each: A. CH3—CH2—CC—CH3 CH3 | B. CH3—C=CH—CH3 C.
Solution Write the IUPAC name for each: A. CH3—CH2—CC—CH3 2-pentyne CH3 | B. CH3—C=CH—CH3 C. 2-methyl-2-butene 3-methylcyclopentene
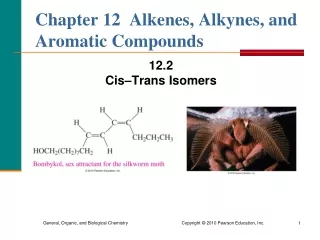
13.3 The Structure of Alkenes: Cis-Trans Isomerism • There is no rotation around the double bond in alkenes. • Groups attached to the double bond are fixed relative to each other. • You can make a “double bond” with your fingers with both thumbs on the same side or opposite from each other.
Cis-Trans Isomers • Two isomers are possible when groups are attached to the double bond. • In a cis isomer, groups are attached on the same side of the double bond. • In the trans isomer, the groups are attached on opposite sides.
Cis-Trans Isomers in Nature • Insects emit tiny quantities of pheromones, which are chemicals that send messages. • The silkworm moth attracts other moths by emitting bombykol, which has one cis and one trans double bond.
Naming Cis-Trans Isomers • The prefixes cis or trans are placed in front of the alkene name when there are cis-trans isomers.cis-1,2-dibromoethene trans-1,2-dibromoethene
Cis-Trans Isomerism • Alkenes cannot have cis-trans isomers if a carbon atom in the double bond is attached to identical groups. Identical Identical 2-bromopropene1,1-dibromoethene
Learning Check Name each, using cis-trans prefixes when needed.
Solution cis-1,2-dibromoethene trans-2-butene 1,1-dichloropropene
13.4 Properties of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.4 Addition Reactions
Addition Reactions • The pi () bond is easily broken, which makes double and triple bonds very reactive. • In the addition reaction, reactants are added to the carbon atoms in the double or triple bond.
Hydrogenation • In hydrogenation, hydrogen atoms add to the carbon atoms of a double bond or triple bond. • A catalyst such as Pt or Ni is used to speed up the reaction.
Hydrogenation of Oils • When hydrogen adds to the double bonds in vegetable oils, the products are solids at room temperature.
Learning Check Write the equation for the addition of hydrogen to 1-butene using a Ni catalyst.
Solution Write the equation for the addition of hydrogen to 1-butene using a Ni catalyst. Ni CH2=CH—CH2—CH3 + H2 CH3—CH2—CH2—CH3
Halogenation • In halogenation, halogen atoms add to the carbon atoms of a double bond or triple bond.
Testing for Double and Triple Bonds • When bromine (Br2) is added to an alkane, the red color of bromine persists. • When bromine (Br2) is added to an alkene or alkyne, the red color of bromine disappears immediately.
Learning Check Write the product of each addition reaction: Pt CH2=CH—CH3 + H2
Solution Write the product of each addition reaction: Pt CH2=CH—CH3 + H2 CH3—CH2—CH3
Hydrohalogenation • In hydrohalogenation, the atoms of a hydrogen halide add to the carbon atoms of a double bond or triple bond.
Markovnikov’s Rule • When an unsymmetrical alkene undergoes hydrohalogenation, the H in HX adds to the carbon in the double bond that has the greater number of H.
Hydration Adds Water • In hydration, H and OH from water add to the carbon atoms of a double bond or triple bond to form alcohols (OH). • The reaction is catalyzed by acid H+.
Learning Check Write the products of each reaction.
Solution Write the products of each reaction.
Polymers Polymers are: • Long-chain molecules. • Found in nature, including cellulose in plants, starches in food, proteins and DNA in the body. • Also synthetic such as polyethylene and polystyrene, Teflon, and nylon.
Polymerization • In polymerization, small repeating units called monomers are bonded to form a long chain polymer. Repeating monomer
Recycling Plastics • Recycling is simplified by using codes on plastic items. 1 PETE Polyethyleneterephtalate 2 HDPE High-density polyethylene 3 PV Polyvinyl chloride 4 LDPE Low-density polyethylene 5 PP Polypropylene 6 PS Polystyrene
Learning Check • What is the starting monomer for polyvinyl chloride (PVC)?
Solution • What is the starting monomer for polyvinyl chloride (PVC)?
Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons 13.6 Aromatic Compounds
13.9 Aromatic Compounds and the Structure of Benzene • Benzene is • An aromatic compound. • A ring of 6 C atoms and 6 H atoms. • A flat ring structure drawn with double bonds. • Represented by two structures because the electrons move among the C atoms.
Benzene Structure • Because the pi electrons in benzene are shared equally among the 6 C atoms, benzene can also be represented as a hexagon with a circle drawn inside.
13.10 Naming Aromatic Compounds • A benzene with a single substituent is often named as a benzene derivative. Methylbenzene Chlorobenzene
Some Common Names • Some substituted benzene rings have common names that have been in use for many years.
Naming Aromatic Compounds • A benzene ring with two or more substituents is numbered to give the lowest numbers to the side groups. • Common names use the prefixes ortho- (1,2-), meta- (1,3-) and para- (1,4-).
Learning Check Select the correct name for each structure: 1) chlorocyclohexane 2) chlorobenzene 3) 1-chlorobenzene 1) 1,3-dichlorobenzene 2) o-dichlorobenzene 3) m-dichlorobenzene
Solution Select the correct name for each structure: 2) Chlorobenzene 1) 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3) m-dichlorobenzene
Learning Check Write the structural formula for each: A. 1-bromo-4-chlorobenzene B. o-chlorotoluene