Understanding the Chain Rule in Single-Variable Calculus
110 likes | 233 Vues
Explore composite functions using the chain rule in calculus with examples and explanations. Learn how to compute f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) efficiently. Dive into concepts like sqrt(x^2+1) and more.

Understanding the Chain Rule in Single-Variable Calculus
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Section 2.5 Chain Rule Math 1231: Single-Variable Calculus
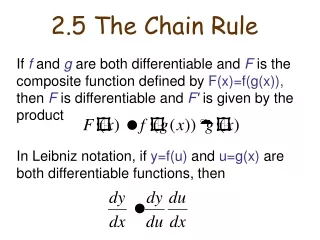
Composite Function Given f(x) and g(x), y = f( g(x) ) is called a composite function, which is denoted by y = f o g (x). Example: f(x) = sqrt(x), g(x) = x2+1, then f o g (x) = f(g) = sqrt(g) = sqrt(x2+1); g o f (x) = g(f) = f2+1 = x + 1. Example: f(x) = sin(x), g(x) = ex, then f o g (x) = f(g) = sin(g) = sin(ex); g o f (x) = g(f) = ef = esin(x); Example: Given y = sqrt(x2+1), find f(x) and g(x) such that f o g = sqrt(x2+1).