Discovering Microscopes: Types, Parts, and Uses
260 likes | 325 Vues
Explore the world of microscopes, from compound to electron microscopes. Learn about lenses, magnification, and microscope parts. Discover how to use a microscope and calculate magnification power.

Discovering Microscopes: Types, Parts, and Uses
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Microscope 2014 - 6th Grade Science
Microscope • A microscope is an instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. • Micro - means very small. • Scope - is a device to look at something. • Uses more than one lens - the image magnified by one lens can be further magnified by another. Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery
How to Make a Simple Microscope • Get 2 magnifying glasses and a sheet of printed paper. • Hold one magnifying glass a short distance above the paper. The image will look a bit larger. • Place the second magnifying glass between your eye and the first magnifying glass. • Move the second glass up or down until the print comes into sharp focus.
Types of Microscopes • Compound Microscope • Containing two or more lenses • Uses light to magnify • High magnification/Low resolution • Most commonly used microscope • $150 - $1,500 • Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) • Used to study parts inside cells • Uses electron beams used to magnify • High magnification/High resolution • $50,000 Examples of Magnification
Microscope Lenses • Lens • Piece of clear material that has been shaped to cause light rays to pass through it to meet or spread out • Concave Lens • A lens that is curved inward • Convex Lens • A lens that is curved outward
Microscope Terms • Magnify • To make an object look bigger • Reflect • To throw back light rays that strike a surface • Refraction • The bending of light rays as they pass through one substance to another
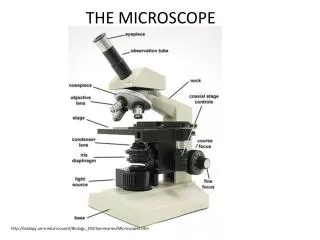
Where you look into the microscope. 1. Eyepiece
Light passes from the objective lens to the eyepiece. 2. Body Tube
The objective lenses are mounted in this part. 3. Rotating Nosepiece
2 or 3 mounted on the nose piece. Each one magnifies a different power. 4. Objective Lenses
This part supports the entire upper portion of the microscope. 5. Arm
You begin your focusing with this part of the microscope. 6. Coarse Adjustment Knob Focus
Once the object that you would like to view comes into focus; you use this to fine tune the image. 7. Fine Adjustment Knob Focus
8. Slide A thin piece of glass where you place a specimen.
The flat place under the objective lens where you place a slide for viewing. 9. Stage
These two things keep the slide from moving around on the stage. 10. Stage Clips
11. Aperture • The opening in the stage that allows light through.
This disk under the stage controls the amount of light that passes through the aperture. 12. Diaphragm
This provides light so that it is easier to see the object that you are viewing. 13. Mirror or Light Source
Supports the microscope and is used to carry it. Bottom part of the microscope. 14. Base
15. Legs • The mirror or lamp is located between these. • Bottom part of the microscope.
Using the Microscope • When carrying a microscope, grasp the arm with one hand and put your other hand under the base. You will NOT move the microscopes in the lab. • Start by adjusting the nosepiece to the lowest power objective tube (the shortest one) • Make sure your slide is on the stage. • Looking through the eyepiece, slowly adjust the coarse adjustment knob until the specimen comes into focus • Make sure the lens does not hit the slide • Slowly adjust the fine adjustment knob until the specimen comes into focus
What’s my power? To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the eyepiece ocular lens by the power of the objective lens. The eyepiece lens usually has a power of 10 x 10 x 40 = 400
What happens as the power of magnification increases? We can see better details with higher the powers of magnification, but we cannot see as much of the image.