Protein-membrane association.
240 likes | 348 Vues
This study explores the theoretical model of protein-membrane associations, employing the Lekner summation technique to accurately compute electrostatic interactions between proteins and lipid membranes. Given the crucial roles these interactions play in biological functions, we discuss the dynamics of integral and peripheral membrane proteins, the thermodynamics of binding free energy, and changes in conformational states. Insights gained from modeling these interactions pave the way for improved understanding of protein behavior at membrane interfaces and can guide future protein-relevant research.

Protein-membrane association.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Protein-membrane association. Theoretical model, Lekner summation A.H. Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi A.H.Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi A.H.Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi A.H.Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi A.H.Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi A.H.Juffer The University of Oulu Finland-Suomi
Previous work • W. Xin and A.H. Juffer, Polarization and dehydration effects in protein-membrane association, To Be Submitted, 2004 • W.Xin and A.H. Juffer, A BEM formulation of biomolecular interaction, To Be Submitted, 2004 • C.M. Shepherd, H.J. Vogel and A.H. Juffer, Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics studies of peptide-bilayer binding, in: High Performance Computing Systems and Applications 2000 (Nikitas J. Dimpoulos and Kin F. Li, Eds.), Kluwer Academic Publishers (Dordrechts, The Netherlands), Chapter 29, 447-464, 2002. • C.M. Shepherd, K.A. Schaus, H.J. Vogel and A.H. Juffer, A Molecular Dynamics Study of Peptide-Bilayer Adsorption. Biophys. J. 80, 579-596, 2001. • A.H. Juffer, C.M. Shepherd and H.J. Vogel, Protein-membrane electrostatic interactions: Application of the Lekner summation technique. J. Chem. Phys. 114, 1892-1905, 2001. • A.H. Juffer, J. de Vlieg and P. Argos, Adsorption of Proteins onto Charged Surfaces: A Monte Carlo Approach with Explicit Ions. J. Comput. Chem., 17, 1783-1803, 1996.
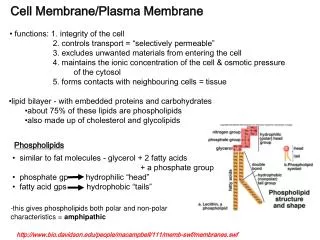
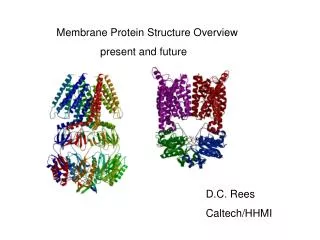
Background • Interactions between lipid molecules and proteins crucial role in regulation biological function. • Membrane proteins: • Integral proteins: e.g. photosynthetic reaction center: • Fully embedded into membrane • Peripheral proteins: e.g. phospholipase C-1: • Only weakly bound to surface, separable by change in pH or ionic strength
Background • Understanding the physics of protein-lipid interactions leads to deeper insight Equilibrium constant ↕ Standard free energy THERMODYNAMICS, NOT MECHANISM
Modeling protein-membrane binding lipid bilayers sandostatin
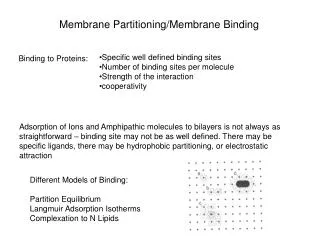
Free energy of binding Conformational Change. Non-polar hydrophobic effect (expulsion of non-polar compounds from water Changes in motional degrees of freedom. Difference in dielectric properties between water and hydrocarbon region (mutual polarization effects). Direct electrostatic interaction between basic residues and anionic lipids. Changes inside membrane.
Coulomb interaction rij + + Long-ranged: beyond dimension of protein
How to calculate it? Assume periodicity along x, y-direction Lx Ly q Image Ly
The Lekner Summation Conditionally converging sum Fast absolutely converging sum
Ions next to flat surface • carrying a negative surface • charge density. • Accumulation of Na+. • Depletion of Cl-. • Electric moment pointing • towards flat surface. • Symmetry along x- and y-axis • but not along z-axis. z-axis
Free energy of adsorption Change in free energy in moving protein from bulk solution at z=- to A point z=z0 near the surface: Thermodynamic integration
Movie The first 2 ns of a 6 ns MD simulation. Biophys. J. 80, 579-596, 2001.
Two solutes A, B immersed in polarizable solvent S Q Solvent cavity q B A approximation
Future improvements • Inclusion of internal (`essential’) degrees of freedom. • Dynamical simulations • Stochastic modeling of proteins • Effects of pH.
Weidong Xin Craig Shepherd Heritage Foundation Human frontiers MRC Biocenter Academy of Finland. Acknowledgements