Understanding Incomplete Dominance, Co-Dominance, and Sex-Linked Traits in Genetics
180 likes | 294 Vues
This guide explores key inheritance patterns in genetics, focusing on incomplete dominance, where the hybrid phenotype is a blend of homozygous phenotypes, exemplified by red (R) and white (r) flowers producing pink (Rr). Co-dominance is also examined, showcasing traits like speckled feathers (BW) when both dominant alleles are expressed. Furthermore, the concept of multiple alleles is discussed through blood types (ABO), along with the importance of Rh antigens in blood transfusions. Lastly, sex-linked traits and the role of polygenic traits in phenotype expression are included for a comprehensive understanding.

Understanding Incomplete Dominance, Co-Dominance, and Sex-Linked Traits in Genetics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
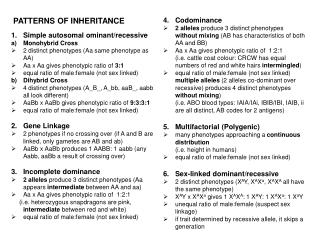
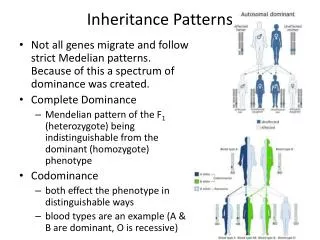
Incomplete Dominance • The heterozygous (hybrid) phenotype is somewhere in-between the homozygous phenotypes • If R = red and r = white • Rr = pink
We still use capital (dominant) and lowercase (recessive) letters • And the same letter!
Co-Dominance • Both alleles of a gene are expressed – Equal dominance (like co-workers) • We write alleles as 2 different capital letters • BB = Black feathers • WW = White feathers • BW = Speckled black and white feathers
Black (BB) White (WW) Black & White (BW)
White (WW) Red (RR) Roan (RW)
Multiple Alleles • A gene that is controlled by 3 or more alleles • Blood Groups – ABO • IA :has only antigen A • IB : has antigen B • i: has neither antigens = Type O • IAIB : has both A and B antigens
Blood Transfusions • Recipient – receives blood • Donor – donates blood • You can only receive blood that has the same antigens on its cells
Rh Antigen • Rh antigen is also found on red blood cells • Do not have antigen = Rh negative • Have antigen = Rh positive
Sex-Linked • Females = XX • Males = XY • If a trait is carried on the X chromosome, a male has only 1 copy • It is more likely that a recessive trait will show up on a male than a female. Why?
Polygenic Traits • Many genes are involved in controlling the phenotype