Negative Contact
400 likes | 557 Vues
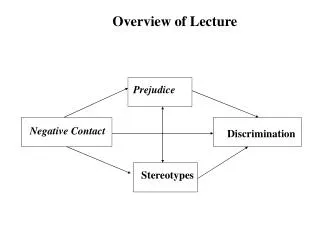
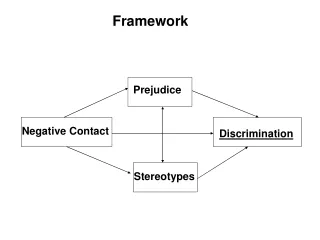
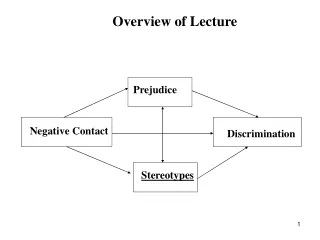
Overview of Lecture. Prejudice. Negative Contact. Discrimination. Stereotypes. What are stereotypes. Associating members of certain groups with certain characteristics E.g., Perceived to be alike; have similar (negative) traits. Stereotypes. Causes of. How to reduce them.

Negative Contact
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Overview of Lecture Prejudice Negative Contact Discrimination Stereotypes
What are stereotypes • Associating members of certain groups with certain characteristics • E.g., Perceived to be alike; have similar (negative) traits
Stereotypes Causes of How to reduce them
Why Stereotypes Form Negative historical relations between groups Inequalities in societal roles Socialization experiences Media portrayals Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Form Negative historical relations between groups • e.g., slavery, indentured labor Inequalities in societal roles • e.g., more women in low-paying jobs, earning less Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Form • Socialization experiences • e.g., parents, teachers, peers • Media portrayals • E.g., African Canadians as “gangsta rappers”, Caribbean Canadians as “ganja” smokers Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Form Negative historical relations between groups Inequalities in societal roles Socialization experiences Media portrayals Stereotypes Causes similar to explaining negative contact
Why Stereotypes Persist • Activated automatically • Reinforced via social norms • Information that confirms beliefs is easily recalled • Trait-based explanations for behavior • Sub-grouping exceptions • Create expectations for interaction • Enable in-group members to feel “different” from out-group members
Why Stereotypes Persist • Activated automatically • E.g., from observable characteristics • Reinforced via social norms • E.g., it is ok to derogate gays nowadays Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Persist • Information that confirms beliefs is easily recalled • E.g., times you saw women driving badly vs. times you saw women driving well Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Persist • Provide trait-based reasons to explain why people behave the way they do • E.g., Women get into more accidents because they are bad drivers • Sub-grouping exceptions of out-group • E.g., successful Black Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Persist • Create expectations for interaction • E.g., Blacks are violent, so this Black man is going to be hostile so I better be prepared Stereotypes
Why Stereotypes Persist • Enable in-group members to feel “different” from out-group members • E.g., Women are bad drivers, Men are good drivers, so they are different Stereotypes
Stereotypes Causes of How to reduce them
How to reduce Stereotypes 1. Stereotypes activated automatically? • Counter automatic activation of stereotypes with guilt (self regulation) • Replace/modify negative associations with positive experiences & information Reduce Stereotypes
How to reduce Stereotypes 2. Reinforced via social norms? • Change old social norms with new ones • Change motivation to comply w/norms Reduce Stereotypes
Information confirming beliefs is easy to recall? Counter recall tendencies with other needs • Make in-group dependent on out-group • e.g., learning to distinguish Chinese editors from each other bec. of supervisory relationship • Create need in in-group members for out-group members to like them • e.g., business case for selling products/services to women Reduce Stereotypes
Trait-based explanations for behavior? Change explanations • Increase focus on situation • E.g., Why are more Blacks in the criminal system? • Different out-group members display non-stereotypical traits in different settings • Teach statistics • Representativeness of sample outgroup member Reduce Stereotypes
Trait-based explanations for behavior? Change explanations • Reduce tendency to blame negative outcomes to out-group members by thinking about out-group in complex ways • E.g., teach about collectivism, power-distance Reduce Stereotypes
Sub-grouping exceptions of out-group? • Increase knowledge of many individual out-groupmembers to prevent sub-group creation • Differentiate out-group members from each other • E.g., cultural circles exercise enabled differentiation by providing contact with different members of the same ethnic group Reduce Stereotypes
Counteract expectations • Out-group members behave in non-stereotypical ways that disconfirm stereotypes • e.g., Women’s driving records • Out-group members confident they do not have the expected trait • e.g., Women is confident of her driving skills • Have expectations for interaction? Reduce Stereotypes
Stereotypes enabling in-group to feel different from out-group? Change ability of stereotypes to maintain differences • Create Super-ordinate Groups • Tendency to view out-group members as alike and negative is no longer functional • Emphasize Multiple Identities • Emphasize those categories which unite groups Reduce Stereotypes
Notice inter-relationships Prejudice Negative Contact Discrimination Stereotypes
Prejudice Negative Feelings Negative Thoughts Negative Associations Stereotypes Positive Associations
Recalling stereotype inconsistent information • Create Super-ordinate groups • Emphasize Multiple Identities • Changing explanations Prejudice Negative Feelings Negative Thoughts Negative Associations Positive Associations Stereotypes
Overview of Lecture Prejudice Negative Contact Discrimination Stereotypes
What is discrimination? • Unequal treatment or behavior toward members of different groups • E.g., Dear White Boss article, Black bosses with black subordinates are more likely to be scrutinized • Qs: Differences in consequences of • Stereotypes vs. prejudice vs. discrimination?
Discrimination Causes of How to reduce it
Attitudes toward discrimination Intention To discriminate Discriminatory Behavior Subjective Norms for Discrimination
What are…. • Attitudes • Thoughts & feelings • Vs Stereotypes? • Vs. Prejudice? • Subjective norms • What do you think other people think/feel about something • Vs. Attitdues?
Belief that discrimination leads to certain outcomes Value of outcomes of discrimination Attitudes toward Discrimination Intention to discriminate
Person’s motivation to comply with others’ wishes Person’s belief that others want person to discriminate Subjective Norms for Discrimination Intention to discriminate
Beliefs that discrimination leads to certain outcomes Attitudes toward discrimination Value of outcomes of discrimination Intention To discriminate Belief that others want target to discriminate Subjective Norm Target’s motivation to comply with others’ wishes
Change beliefs about rewards vs. costs of discriminatory behavior • e.g., expectation of reward for hiring visible minorities Change Attitudes toward discrimination • Change value of outcomes of discrimination • e.g., lawsuits for discrimination
Change beliefs about rewards vs. costs of discriminatory behavior • Change awareness of definition & results of discrimination • E.g., Using “weight” as a criterion for hiring can result in lawsuit if “weight” is not established as a BFOQ Change Attitudes Change value of outcomes of discrimination
Change norm e.g., CEO’s public behavior Change person’s motivation to comply with (unchanged) norm Change perception of norm (awareness) Subjective Norms for Discrimination Intention to discriminate
Change perceptions of costs of discriminating against Gays • E.g., Removal of student from residence hall for repeat offences, or in-admission into residence halls in subsequent years Attitudes toward gays Intention to Discriminate Against gays Change belief that others Approve of discrimination Toward gays e.g., Popular (influential) students’ beliefs about gay harassment Subjective Norm to Discriminate against gays
Discriminatory Attitude Non-discriminatory behavior Dissonance Discomfort Derogate “non-performed” alternative (attitude) Change Attitude toward discrimination to be consistent with behavior
Non discriminatory behaviors • Choose to argue against your position voluntarily • Cooperate w/ outgroup Attitude for discrimination Dissonance Insufficient justification for voluntary behavior Change Attitude toward discrimination
Overview of Lecture Prejudice Negative Contact Discrimination Stereotypes