Cellular Respiration
370 likes | 406 Vues
Learn about the process of cellular respiration and how it is connected to photosynthesis. Discover the end products of photosynthesis and their importance in producing ATP, the energy molecule used by all living organisms. Explore the two types of cellular respiration and understand how glucose is converted into ATP.

Cellular Respiration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
from Photosynthesis to Cell Respiration • What are the end products of Photosynthesis? _______________________ • Why are these products important (how are they used)? _______________________________________________
What is Cellular Respiration? It is a PROCESS ALL organisms (including plants) perform cell respiration! • Cellular Respiration is how every cell changes Glucose into ATP. ATP is the cell’s energy molecule. • ATP is used by cells to perform ALL biological activities! (STRANGER-C)
Cellular Respiration • Respiration occurs in ALL cells and can take place with or without oxygen present
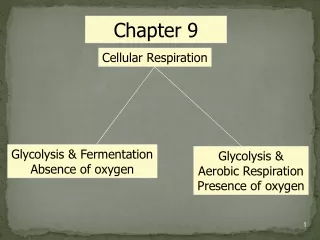
TWO TYPES • Cellular respiration is the process in which glucose is used to produce cell energy • This energy-releasing process takes place in ALL living cells (plant AND animal!) Two types: Aerobic - with oxygen Anaerobic - without oxygen
What's happening? • During cell respiration, glucose is broken down to create a high-energy molecule called “ATP” • Carbon dioxide and water are waste products of this process • Hank - Cell Respiration
SUNLIGHT TO ATP • During Photosynthesis, radiant energy is captured and stored in the bonds of Glucose • During Cell Respiration, the energy in Glucose is transferred to a molecule of Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) ATP is the energy molecule for ALL living organisms (plant AND animal)
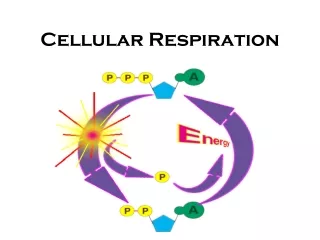
Adenine Ribose 3 Phosphate groups CELL ENERGY (ATP) • : • ALLorganisms use Glucose to create a more “usable” form of energy called ATP • ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate • ATP is the energy molecule for ALL living things!
Adenine Ribose 2 Phosphate groups CELL ENERGY (ATP - ADP) • In the Mitochondria, ATP is converted to ADP when energy is needed • ADP stands for adenosine diphosphate • Breaking a Phosphate group off of ATP releases the energy that is stored in that bond
ATP to ADP AND BACK AGAIN • All energy is stored in the bonds of compounds —breaking the bond releases the energy • When the cell has energy to store it adds a phosphate group to ADP - producing ATP • When the cell needs energy for life processes, it breaks the bond holding the phosphate group and changes ATP back to ADP • Adding a bond stores energy • Breaking a bond releases energy
ATP to ADP AND BACK AGAIN • It’s almost like recharging your cell phone!
Aerobic Cellular Respiration • In most Eukaryotic organisms, cell respiration requires oxygen. • This is aerobic cellular respiration. • In aerobic respiration, glucose is broken down completely into ATP, carbon dioxide and water. • This is an efficient process which makes 36 ATP molecules from one Glucose molecule. aerobic exercise
Formula for Aerobic Cell Respiration C6H12O6 + O2 ----> H2O + CO2 + 36 ATP • 1 Glucose molecule and 2 ATPs are needed to start the process • Aerobic (with oxygen) is very efficient! 1 Glucose makes 36 ATP molecules!
Do you notice something about this equation? • It’s the opposite of the Equation for Photosynthesis! O2 + C6H12O6 H2O + CO2 + ATP CO2 + H2O + Energy C6H12O6 + O2
Plants and Animals Rely on each other! • Animals use: • Glucose (from producers/plants) • Oxygen (from producers/plants) • Plants use: • Carbon dioxide (from consumers/animals) • Water (from consumers/ animals)
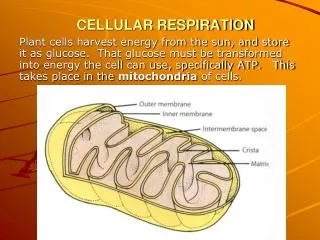
Where does this happen? • Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria. (That's why we call this organelle the “mighty mitochondria – because it is the “powerhouse” of the cell!) mighty mouse saves the day • Mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells. **Cells that need more energy (muscle cells) have more mitochondria**
The mitochondria change the O2 and Glucose O2 O2 O2 O2 O2
Glycolysis • Before aerobic cellular respiration can occur, an initial step, called glycolysis, takes place outside the mitochondria, in the cytoplasm • What do the letters “LYS” stand for???? __________________ • “GLYC” stands for glucose… • What do you think Glycolysis means? _______________________________
Glycolysis • The Mitochondria are covered by a selectively permeable membrane • Glucose is too big to fit through the pores • In Glycolysis, the Glucose molecule is broken into two molecules of Pyruvate Remember…Glyco stands for “Glucose”... “lys” means destroy • This occurs in the cytoplasm
Glycolysis • Remember Diffusion???? • In order for the molecule to DIFFUSE, it has to FIT through the membrane! • So… Glucose has to be chopped in half! • It becomes two molecules of Pyruvic Acid (Pyruvate)
Glycolysis In glycolysis, Glucose is broken down so it can diffuse into the mitochondria. Which is a bigger, more complex molecule? ?????????? ??????????
GLYCOLYSIS… • Glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate (aka pyruvic acid) • This step occurs before either anaerobic or aerobic cellular respiration • 2 ATP are needed to “chop” glucose! • The pyruvate then enters the mitochondria, where aerobic cellular respiration occurs
Aerobic Cell Respiration • There are two steps which happen after glycolysis: • The Krebs cycle, or citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain (ETC) • Both happen inside the mitochondria • Overall, at the end of these three steps, there is a net gain of 36 ATP molecules.
Krebs Cycle • The Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) requires oxygen • This is where Carbon Dioxide is formed • Think: Krebs = Carbon • This part of the process takes place in the mitochondria
Electron Transport Chain (ETC) • Electrons are passed through the membrane of the mitochondria • They bind with 2 H+ ions and Oxygen to form a molecule of H2O • Remember? Bonding through dehydration synthesis!
Anaerobic Respiration • When there is no oxygen, cell respiration consists of two pathways: • Glycolysis and Fermentation. • Both of these occur in the cytoplasm and only produce 2 ATPs
Anaerobic Respiration • Anaerobic Respiration is also called Fermentation • 2 Types: Alcoholic & Lactic Acid
Anaerobic Respiration • Fermentation is used in the baking and brewing industries • It occurs with yeast and bacteria, but will occur in animals (humans) under certain conditions • Depending on the organism, there are different end products from the breakdown of glucose
Anaerobic Respiration Equations(Fermentation) • In Plants (Yeast): • Pyruvate ---> Alcohol + CO2 • In Animals (Bacteria & Muscle Cells): • Pyruvate ---> Lactic Acid
In Plants (yeast) • Yeast is used in the baking and brewing industries • To make Bread, Beer and Wine • As yeast perform anaerobic respiration, they convert glucose into ethanol alcohol with CO2 as a bi-product
Bacteria & Muscles…. • Bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Bacteria convert glucose into lactic acid • The same happens in overworked muscle cells! • Ever feel the “burn” in your muscles after working out??? • That’s Lactic Acid!
In Animals (humans!!!!) • Ever run in gym class and feel a burning in your legs? • How about lifting weights? Do your arm and chest muscles ever burn while you are working out? • That burning sensation is muscle fatigue – and it's caused by lactic acid build-up!
Muscle Fatigue • During exercise, muscle cells use oxygen faster than your body can supply it! • To get more energy, the muscle cells convert to anaerobic respiration • This causes a build up of lactic acid in the muscle tissue – acid “burns” and your muscles feel “sore”
Review Questions • What is cell respiration? ________________________________________________________________ • The waste products of aerobic cell respiration are: ______________ & _______________ • The energy from glucose is transferred by cell respiration into energy molecules called ___________ • In what organelle does cell respiration occur? ____________
More.... • The process of _______________ cellular respiration does NOT require oxygen. • The process of _______________ cellular respiration DOES require oxygen. • Another name for anaerobic cell respiration is ____________________. • The end products of fermentation are • ____________ & either ____________ OR _____________