Biological Chemistry
410 likes | 528 Vues
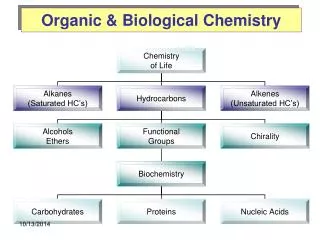
Water, a polar molecule making up 50-75% of body weight, plays a critical role as a universal solvent in biological systems. It exhibits unique properties such as cohesion, adhesion, and thermal stability. Organic chemistry encompasses vital biomolecules: carbohydrates (saccharides), lipids (fats, oils), proteins (peptides, amino acids), and nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) that are essential for cellular function. Each class of molecules has distinct properties and functions, influencing energy storage, cellular structure, and biochemical reactions crucial for life.

Biological Chemistry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Water • Polar Molecule that creates 50-75% body weight • Polar Molecule: ? • b/c polar, held together by weak H+ bonds
Functions of Water • Universal Solvent • Cohesive • Adhesive • Reactivity • Thermal Stabilty
Mixtures with Water • Solution: solute ( less than 1 nm )mixed with solvent • Colloid: 1-100nm molecule mixed with water • Suspension: over 100 nm molecule suspended in water • Emulsion: combination of water with hydrophobic liquid
Organic Chemistry • Carbohydrates: Saccharides: CHO • Fats: Lipids • Triglycerides • Phospholipids • Eicosanoids • Sterol Proteins: Peptides
Carbohydrates • Monosaccharides: C6H12O6 • Disaccharides: C12H22O11 + H2O • Polysaccharides • Starches • Glycogen • Cellulose
Cellular Respiration • Glycolysis
Lipids • Hydrophobic molecules • Less oxidized than carbohydrates….therefore more caloric value • Energy lipids vs. non-energy lipids
Saturated Fatty Acids 10% • Carry maximal hydrogen • Long chain fatty acid: solid at room temp. • Short chain saturated fats: liquid at room temp. (e.g., coconut oil)
Monounsaturated Fats 10% • Has 1 C=C • Short chain fatty acids = what physical characteristic? • CaproleicAcid • Lauroleic Acid • Myristoleic Acid • Palmoteic Acid • Oleic Acid (Omega 9) • Eruric Acid (Omega 9)
Omega 9 Fatty Acids • Terminal double bond at 9 carbon • Not considered essential • b/c no n6 bond….does not promote eicosanoids • Olive oil, canola, rapeseed, mustard oil
Polyunsaturated Fats 10% • 2 or more C=C • Contain Essential PUFAs: • Omega 3 • Omega 6
Omega 3 • Alpha Linolenic Acid n-3 • Sources: soybean oil, canola oil, walnuts, wheat germ, flax, fishes, chia, hemp seeds, algaes, leaves • Converted by liver into : • Eicosapantaenic Acid • Docoshexanoic Acid
Functions • Neurological development • Reduce vascular disease • Reduce tumor growth • Reduce inflammation • Reduce CVD • Improved immune function • Cell structure
Omega 6 • Linoleic Acid n-6 • Sources: most vegetable oil, nuts, seeds • Converted by the liver: • Arachidoic Acid • Docosopantanoic Acid
Functions • Promotes dermal integrity • Visual health • Cell structure
Problems Associated • Proinflammatory • Eicosanoid: • Leukotrienes: inflammation • Thromboxane: platelet aggregation • Prostanglandins: immune and inflammation response
Diseases Associated • CVD • CHD • Cancer • Artherosclerosis • Alzheimers • Obesity • Diabetes • ADHD • Stroke • Arthritis • Osteoporosis • ETC!!!
Structural Comparison • Trans position • Rigid • Cis-position • Fluid
Dangers • Promotes increased Coronary Heart Disease (1956) and Cardiovascular Disease by increasing LDL and decreasing HDL • New England Journal of Medicine • National Academy of Science
Structural Fats Phospholipids and Cholesterol
Eicosanoids • Signaling molecules created from the oxidation of 20 carbon fatty acids • Linked to inflammation
Peptides • Peptides are polymer chains composed of amino acid monomers joined by peptide bonds
Essential Amino Acids(9) • Cannot produce • Must be derived from exogenous sources • Histidine • Isoleucine • Leucine • Lysine • Methionine • Phenylalanine • Threonine • Typtophan • Valine
Nonessential Amino Acids(11) • Can produce endogenously • Alanine • Arginine • Asparagine • Aspartic Acid • Cysteine • Glutamic Acid • Glutamine • Glycine • Proline • Serine • Tyrosine
Polypeptide Function • Nitrogen balance • Fluid balance • Enzymes • pH balance • Blood Clotting • Hormones • Antibodies • Protein Synthesis • Gluconeogenesis
Nucleic Acids • DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid • RNA: Ribonucleic Acid • Nucleotide monomers joined by covalent bonds • Responsible for transfer of genetic material