Understanding Capacitors: Charging, Discharging, and Circuit Analysis
270 likes | 436 Vues
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamentals of capacitors, including their construction, symbols, charging, and discharging processes. Learn how positive and negative charges interact and the significance of fringe fields in circuits. The impact of different light bulbs on capacitor charging is discussed, alongside definitions of capacitance and practical calculations involving capacitor plates. Additionally, discover how to use multimeters to measure current, voltage, and resistance in various circuits, with insights on RC circuits and time constants.

Understanding Capacitors: Charging, Discharging, and Circuit Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Capacitor: Charging and Discharging Charging Discharging
Capacitor: Construction and Symbols The capacitor in your set is similar to a large two-disk capacitor D s There is no connecting path through a capacitor
How is Discharging Possible? Positive and negative charges are attracted to each other: how can they leave the plates? Fringe field is not zero! Electrons in the wire near the negative plate feel a force that moves them away from the negative plate. Electrons near the positive plate are attracted towards it.
Capacitor: Charging Why does current ultimately stop flowing in the circuit? Ultimately, the fringe field of the capacitor and the field due to charges on the wire are such that E=0 inside the wire. At this point, i=0.
The Effect of Different Light Bulbs Thin filament Thick filament Which light bulb will glow longer? Why? • Round is brighter capacitor gets charged more? 2) Long bulb glows longer capacitor gets charged more?
An Isolated Light Bulb Will it glow at all? How do electrons flow through the bulb? Why do we show charges near bulb as - on the left and + on the right?
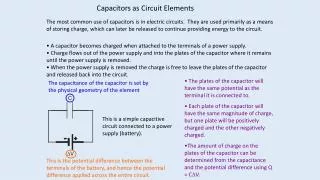
Capacitance -Q +Q E s Electric field in a capacitor: In general: Definition of capacitance: Capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor: Capacitance
Capacitance Units: C/V, Farads (F) Michael Faraday (1791 - 1867)
Exercise The capacitor in your set is equivalent to a large two-disk capacitor D s=1 mm How large would it be? D ~ 10 km (6 miles)
Exercise A capacitor is formed by two rectangular plates 50 cm by 30 cm, and the gap between the plates is 0.25 mm. What is its capacitance?
A Capacitor With an Insulator Between the Plates D s No insulator: With insulator:
Ammeters, Voltmeters and Ohmmeters Ammeter: measures current I Voltmeter: measures voltage difference V Ohmmeter: measures resistance R
Using an Ammeter 0.150 Connecting ammeter: Conventional current must flow into the ‘+’ terminal and emerge from the ‘-’ terminal to result in positive reading.
Ammeter Design Simple ammeter using your lab kit: Simple commercial ammeter Digital ammeters: uses semiconductor elements. ADC – analog-to-digital converter (Combination of comparator and DAC)
Voltmeter Voltmeters measure potential difference VAB – add a series resistor to ammeter Measure I and convert to VAB=IR Connecting Voltmeter: Higher potential must be connected to the ‘+’ socket and lower one to the ‘-’ socket to result in positive reading.
Ohmmeter A R Ohmmeter How would you measure R? Ammeter with a small voltage source
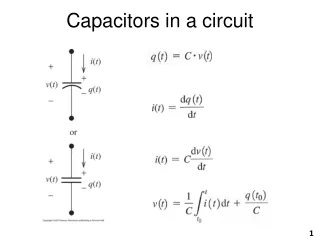
Quantitative Analysis of an RC Circuit Initial situation:Q=0 Q and I are changing in time
RC Circuit: Current Current in an RC circuit Current in an RC circuit What is I0 ?
RC Circuit: Charge and Voltage Current in an RC circuit What about charge Q?
RC Circuit: Summary Current in an RC circuit Charge in an RC circuit Voltage in an RC circuit
The RC Time Constant Current in an RC circuit When time t = RC, the current I drops by a factor of e. RC is the ‘time constant’ of an RC circuit. A rough measurement of how long it takes to reach final equilibrium
What is the value of RC? About 9 seconds
A B D C
Exercise Current in an RC circuit What is the final charge on a 1 F capacitor connected to a 1.5V battery through resistor 100 ? Can you apply the RC equations to the circuit below? No! Resistance depends on current.
Exercise: A Complicated Resistive Circuit I2 I1 I3 Loop 1 Loop 2 Loop 3 I4 I5 Loop 4 Find currents through resistors loop 1: loop 2: loop 3: nodes: Five independent equations and five unknowns