Types of Vegetative Propagation
150 likes | 1.62k Vues
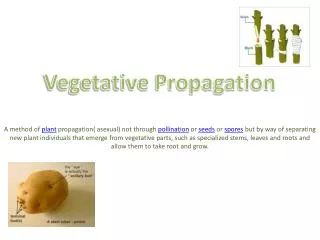
Cuttings (stem cuttings, leaf cutting, root cuttings): Begonias, Gardenias, Pineapples, Coleus Separation/Division : Irises, Sempervivum, Lilies Grafting : Roses, Walnuts, Apples, Apricots Layering : Diffenbachia, Rubber Tree ( Ficus elastica ). Types of Vegetative Propagation.

Types of Vegetative Propagation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cuttings (stem cuttings, leaf cutting, root cuttings): Begonias, Gardenias, Pineapples, Coleus Separation/Division: Irises, Sempervivum, Lilies Grafting: Roses, Walnuts, Apples, Apricots Layering: Diffenbachia, Rubber Tree (Ficus elastica) Types of Vegetative Propagation
Stem Cuttings • Use sections of the stem which have leaves. • Treat with rooting hormone to promote root growth.
Leaf Cuttings • Uses a leaf section, petiole, or a cutting of the leaf. • The cutting is then treated with hormones to stimulate root growth.
Root Cuttings • A section of the root is cut and planted. • A new plant grows from the root cutting.
Layering • This method is used mainly with plants which naturally reproduce this way (blackberries & vines). • A section of the stem is scraped and buried. • Roots grow from the buried stem.
Separation • The removal of corms or bulblets from a parent plant. • The small corm or bulb is then used for planting
Division • Roots and shoots of plants which grow in bunches are dug up and separated. • The divisions are planted.
Grafting • Material from two different woody plants are directly joined. • Used to create plants with disease resistant or dwarfing root stocks. • Plants are specially cut and spliced together.