Tissue Engineering: Cell aggregates
110 likes | 443 Vues
Tissue Engineering: Cell aggregates. Thesis project Chemical and Process Engineering Ph.D. program ETSEQ Rovira i Virgili University. Student: Verónica Saravia Supervisor: Petros Lenas February 2005. What is “ Tissue engineering ”?.

Tissue Engineering: Cell aggregates
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tissue Engineering:Cell aggregates Thesis project Chemical and Process Engineering Ph.D. program ETSEQ Rovira i Virgili University Student: Verónica Saravia Supervisor: Petros Lenas February 2005
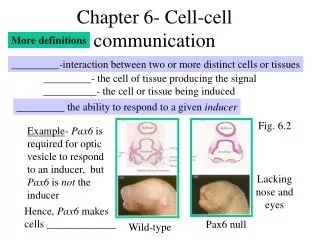
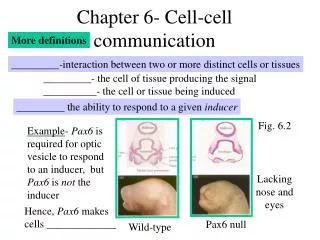
What is “Tissue engineering”? • fundamental understanding of structure-function relationships in tissue • development of biological substitutes to restore, or improve tissue function IntroductionObjectives Methodology Future work
IN VIVO • Metabolic heterogeneity • Cooperatively Introduction IntroductionObjectives Methodology Future work
IN VITRO • 2-D Vs 3-D Cell aggregate COMPLEXITY Introduction IntroductionObjectives Methodology Future work
LONG TERM OBJECTIVE • Synthesize in vitro part of the structural complexity of a tissue using cell aggregates and different systems configurations of increasing complexity. DEA SCOPE • Production of different cell aggregates • Characterization of the aggregates Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Methodology: Aggregates production Assay Evaluation • Cells: HepG2 • Medium: DMEM +FBS +non essential AA +Glutamine + Anti-biotic • RWV reactor • Cell quantification • Viability • Glucose consumption • Geometry • Toxicology assays with APAP • Rotation speed • Culture time • Aggregation form • Toxicology results Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Rotary Cell Culture System • Advantages: • low shear stress • high mass transfer rates Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Responses: • Growth curve Variables: • Aggregate type • Culture conditions: • Rotation speed • Culture time • Viability • Geometry characteristics • Toxicity results Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Toxicology test • Toxicant: • APAP ant-inflammatory drug hepatoxicity in vivo and in vitro • Assays: • cell quantification • cell viability • others Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Future work Design, implementation and development of models of in vitro systems, using different systems configurations of increasing complexity. Introduction Objectives Methodology Future work
Any questions... THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION!