Understanding Truth Tables: Conjunctions, Disjunctions, and Compound Statements
220 likes | 420 Vues
Dive into the intriguing world of truth tables, essential for evaluating compound statements in logic. This guide will explore the concepts of conjunctions and disjunctions, highlighting their distinct definitions, symbols, and truth conditions. Conjunctions, represented by "and" (^) are true only when all components are true, while disjunctions, denoted by "or" (v), are true if at least one component is true. Discover how to create and analyze truth tables, including examples, to deepen your understanding of tautologies and contradictions.

Understanding Truth Tables: Conjunctions, Disjunctions, and Compound Statements
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Notes - Truth Tables fun, fun, and more fun!!!!
A compound statement • is created by combining two or more statements, p and q.
Conjunction • uses the word “ and” • Symbol ^ • True only when all parts are true
Disjunction • uses the word “or” • Symbol v • True if any one of its parts are true
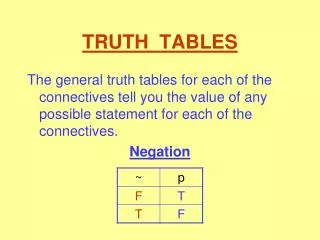
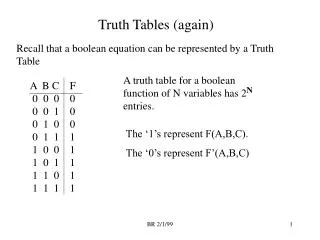
truth table • a table that lists all possible combinations of truth values • ****Be sure to include all possible combinations of truth values for each piece of the compound statement***
A statement whose truth table contains only True in the final column is a tautology • A statement whose truth table contains only False in the final column is a contradiction