DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter)
110 likes | 426 Vues
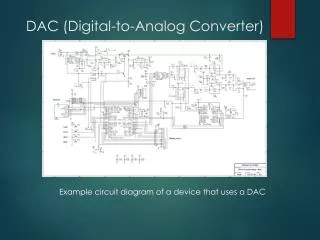
DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter). Example circuit diagram of a device that uses a DAC. PMP Circuit Diagram. This is a custom made portable media/music player (PMP). Source: http://elm-chan.org/works/pcmp/report.html. PMP Circuit Diagram (cont.). The DAC used in this particular PMP.

DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) Example circuit diagram of a device that uses a DAC
PMP Circuit Diagram This is a custom made portable media/music player (PMP) Source: http://elm-chan.org/works/pcmp/report.html
PMP Circuit Diagram (cont.) The DAC used in this particular PMP
PMP Circuit Diagram (simplified) Simplified diagram of the PMP showing primary components
What is a “DAC”? (cont.) • Stands for Digital-to-Analog Converter • Converts digital signals to analog signals • In this case, audio signals are converted • Used with almost all devices that outputs sound • Phones, portable media players (PMPs), TVs, etc. DACs are usually denoted with this symbol DAC INPUT OUTPUT
DACs in other electronics • DACs are not only used for sound, but also for video • Video data is converted into electrical signals/pulse that drives the display dictating what color and brightness each pixel emits • Devices that interacts with the physical world will likely have a DAC • Example: automatic lights use DACs • Most devices also have an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) along with an DAC • ADCs are opposite of DACs in which they instead converter analog signals to digital
Process Flow Layout • A digital system can be anything that interprets digital inputs • Example: computers, media players, TVs Physical Variable 2 3 4 5 Digital System DAC ADC 1 Actuator Transducer To control physical variable Electrical Analog Signal Digital Inputs Digital Output Analog Output
What is a “DAC”? (cont.) D DAC A Digital to Analog Converter Implemented as integrated circuits (IC) (in most cases) Analog (Op Amp) Digital Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) Source: see source reference
Analog vs Digital Analog signal is smooth and continuous and digital is more discrete at any given time interval Analog Digital
Analog vs Digital (cont.) • Digital signals can be processed and manipulated by computers and other electronic • Analog (electric) signals are needed to produce sound • There is a loss of data when converting analog to digital signals • A reconstruction filter, usually a form of interpolation, is frequently used to fill in missing data • Used when converting to analog signals • Interpolation also smooth out the jagged digital signal
Analog vs Digital (cont.) In this case, the digital signal produced by the player is then converted into analog electrical signal. The signal then goes though an amplifier and to the speakers, headphones, etc.