Understanding the Urinary System: Anatomy and Functions
1.09k likes | 1.21k Vues
The urinary system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. It comprises the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, functioning to regulate blood and water volume, blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and acid-base balance. Key components include nephrons, which are responsible for filtering blood and forming urine. Aging affects the urinary system's efficiency, leading to various conditions such as incontinence and urinary tract infections. This overview covers normal urine composition, diagnostic tests, and common urinary disorders, emphasizing the importance of urinary health.

Understanding the Urinary System: Anatomy and Functions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
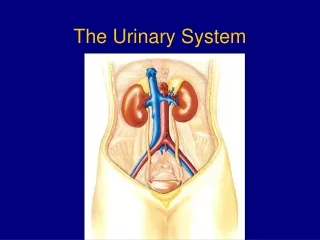
The Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology 2014
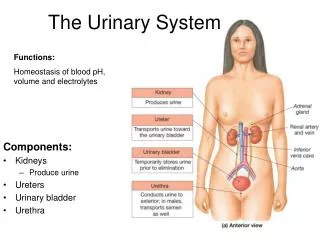
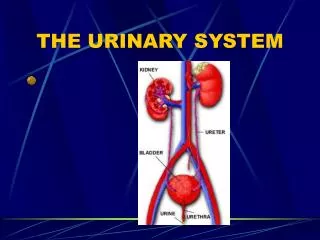
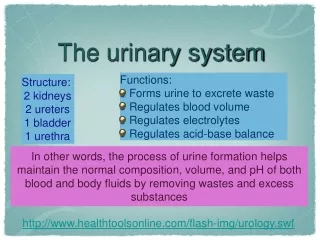
Structure • Kidneys • Ureters • Urinary bladder • urethra
Function • Maintains homeostasis • Controls blood and water volume • Maintains blood pressure • Regulates electrolyte levels
Eliminates protein wastes, excess salts and toxic materials from blood • Balances acid/base (PH) • Secretes renin and erythropoietin
Kidney Structure • 2 reddish brown, bean-shaped organs • Located in small of the back at lower edge of ribs on either side of spine • “Retroperitoneal”
How the kidneys Regulate BP • ADH • RENIN • ALDOSTERONE
3 Parts • Cortex • Medulla • Pelvis
Nephron • Functional units of the kidney • Cells that form urine • Over 1 million nephrons in each kidney
Glomerular Filtration • Tubular Reabsorption • Tubular Secretion
WORD WALL • Oliguria • Anuria • Dysuria • Polyuria • hematuria
Urine • Body excretes 1000-2000 ml of urine/day • Is normally sterile • Color varies with hydration
Characteristics of Normal Urine • CLARITY • ODOR • SPECIFIC GRAVITY
THINK…. • A STRONG, OFFENSIVE ODOR FROM FRESHLYVOIDED URINE IS SUGGESTIVE OF…….. Urinary Tract Infection
Composition of Normal Urine • Water • Protein wastes products (urea, uric acid & creatinine) • Excessive minerals from diet (Na+,K+, Ca,sulfates & phosphates
Toxins • Hormones • Bile compounds • Pigments from food/drugs
WORD WALL • Frequency • Urgency • Nocturia • Enuresis • retention
Effects of Aging on the Urinary System • Ability to filter blood, reabsorb electrolytes & secrete wastes decreases • Less ability to return to normal after changes in blood volume
Decrease in number & size of nephrons • Decrease in GFR • Smaller capacity of bladder • Weaker bladder muscles
Incontinence • Not a normal consequence of age • Common due to many reasons • See Chpter 23 for more information on incontinence
Critical Thinking Challenge COMPARE & CONTRAST COMPARE & CONTRAST URGE vs. OVERFLOW • STRESS vs. FUNCTIONAL
Nursing Assessmentof The Urinary System
HEALTH HISTORY • Chief complaint • History of Present Illness • Past Medical History • Family History • Review of Systems
Diagnostic & Laboratory Tests Urinary System
URINE TESTS • UA ( urinalysis ) • C & S ( Culture & Sensitivity ) • Creatinine Clearance (24 hr)
BLOOD TESTS • BUN ( blood urea nitrogen ) • Serum Creatinine • Serum Electrolytes
Radiographic Studies • KUB ( flat plate ) • IVP • Arteriogram • Renal Scan • US
Invasive Procedures • Renal Biopsy • Cystoscopy
What are Urodynamic Studies ??
What are common Therapeutic measures Related to “Catheterization”
Catheter Types Foley Ureteral Suprapubic Nephrostomy
Common Tubes and Catheters • Ureteral Catheter • Nephrostomy Tube • Urinary Stent
Pre-Op Care Urologic Surgery • Evaluate fluid status • Bowel cleansing • Enterostomal Therapist/Nurse • Counseling/Teaching
Post-Op Care Urologic Surgery • Report to MD U/O < 30 ml/hr • Pain Management • Mon. lung sounds • Assess for Paralytic ileus
Urinary Tract Inflammation and Infections
Cystitis • Inflammation of the urinary bladder • Bacteria enters from the urethra, lymph nodes, infected kidneys • Women more suseptible
Causes • E-coli • Candida Albicans • Coitus • Diabetes mellitus • See Box 40-2 Risk Factors for UTI’s
Signs & Symptoms • Dysuria, hematuria • Frequency, urgency • Low grade fever • Pelvic or abd. discomfort • Bladder spasms
Med. Dx & Tx • C&S and UA obtained • Increase fluids 3-4 L / day • Antibiotics (Cipro,Bactrim,Septra • Analgesics(Pyridium) • See Pt. Teaching pg. 898
Gerontologic Considerations • Watch for signs of mental confusion • Fever may be masked • Sepsis develops quickly
Pyelonephritis • Bacterial infection of renal pelvis and kidney • Most common form of kidney disease • Often the result of reflux
Signs & Symptoms • Flank pain • Chills, fever,N & V • Dysuria, fatique • Bladder irritation
Med & Nursing Considerations • Bedrest • Increase fluids (8 8oz. Glasses water/day) • IV • Monitor I + O • Protein & Na+ restrictions • Mon. for circulatory overload
Pharmacological TX • Antibiotics (Bactrim) or Cipro • Antipyretics • Analgesics • Antispasmotics • Antihypertensives
Glomerulonephritis • Autoimmune disease • Glomerulus becomes inflammed • Symptoms dev. 1-3 wks after respiratory infection cau by group A- hemolytic strep
Signs & Symptoms • Tea colored urine • Decrease in u/o • Periobital edema • HTN • Hypervolemia