Visual Perception
190 likes | 391 Vues
Visual Perception. Chapter 3. Sensation & Perception. Sensation: Occurs when our sensors (internal & external) detect & respond to information. Perception : assigning meaning to the information that we sense. This occurs in the brain and is a personal interpretation.

Visual Perception
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Visual Perception Chapter 3
Sensation & Perception Sensation: Occurs when our sensors (internal & external) detect & respond to information. Perception: assigning meaning to the information that we sense. This occurs in the brain and is a personal interpretation. When you view the next 3 images, your eyes will gather information, then you brain will select certain parts of that information, organise the parts and finally interpret and evaluate them.
Role of the eye in Visual Perception • View clip on the eye
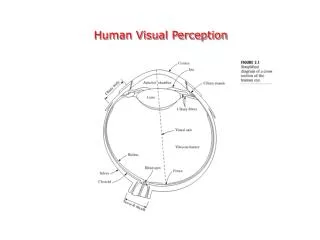
Reception, Transduction, Transmission • Reception: photoreceptors (rods & cones) in the retina detect light stimulus • Transduction: Light energy (EM) is converted into electrochemical energy • Transmission: Electrical message is sent to the visual cortex in the brain via the optic nerve. AT 2: From Light To Lobe Movie clip: Sensation & perception
Perception: Gestalt principles • Gestalt – the way we organise parts into a whole • We mentally ‘fill in’ the parts that we can’t see. 1. figure-ground organisation • Object is the figure, everything else is background • Needs a line or boundary (contour) • Contour is part of the object
Perception: Gestalt principles 2. Closure • tendency to mentally fill in or ignore gaps in the object 3. Similarity • Tendency to group similar features together
Perception:Depth principles 4. Proximity • tendency to perceive parts that are close together as belonging together.
Perception:Depth principles • Ability to accurately estimate the distance of an object (can see 3-D) • Binocular (requires both eyes) • Convergence • Retinal disparity
Perception:Depth principles • Ability to accurately estimate the distance of an object (can see 3-D) 2. Monocular (requires only one eye) • Accommodation • Pictorial Cues • linear perspective • interposition • texture gradient • relative size • height in the visual field
Perception:Perceptual constancies 3. Perceptual Constancies • shape constancy • size constancy • brightness constancy
Explorations • http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/chvision.html • http://academics.tjhsst.edu/psych/oldPsych/perception/ • Folio Activity: Stroop Effect • http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/words.html