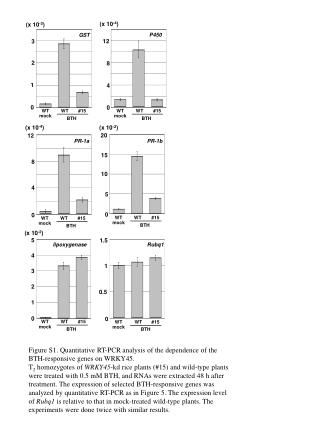
gst protein induction
40 likes | 60 Vues
Profacgen provides professional service for protein pull down assay. We have technical service group and most advanced instruments to perform the entire procedure with high-efficiency and high-quality.<br><br>Background<br><br>Pull down assay is an in vitro method to detect protein-protein interaction. The commonly used bait protein is a purified GST-tag protein. Pull down assay is usually followed by SDS-PAGE and Mass Spectrometry (MS) analysis to identify the interactor, and further genetic approaches or Western Blot analysis can be implemented to confirm the direct interaction.

gst protein induction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Gst protein induction Pull Down Assay INQUIRY Profacgen provides professional service for protein pull down assay. We have technical service group and most advanced instruments to perform the entire procedure with high-efficiency and high-quality. Background Pull down assay is an in vitro method to detect protein-protein interaction. The commonly used bait protein is a purified GST-tag protein. Pull down assay is usually followed by SDS-PAGE and Mass Spectrometry (MS) analysis to identify the interactor, and further genetic approaches or Western Blot analysis can be implemented to confirm the direct interaction. Feature The following figure shows the feature of pull down assay. Pull down assay Comparison Between Pull Down Assay and Co-IP Pull down assay Experimental design Sample You can provide us crude tissue sample or cell sample. Tag preference GST tag is the most preferred for bait protein purification, you can also use biotin tag or maltose binding protein (MBP) tag. His-tag is not available, since the metal affinity beads will bind proteins non-specifically. Control
All necessary control groups will be included according to the following table to verify interaction specificity. Pull down assay Customized service: Experimental design We will elaborately design our experimental scheme according to the protein of your interest, for example, its structure and function domain, cellular function, enzymatic or other activity, etc. Specificity Sometimes control samples are needed to increase the specificity of pull down assay. You can provide us a series of truncations, deletions, mutations of your purified tag fusion protein, or even related proteins from other genes. Whether cross-link is needed We will include the cross-linking (tagged protein with beads) step into the entire procedure or not, based on your requirement. The additional cross-linking step will make the final analysis more easily: since the tag fusion protein is covalently linked to the bead and will not appear in the subsequent gels. But please note: loss of some or all biological activity of specific proteins (particularly enzymes) may occur as a result of the chemical modification that occurs during cross-linking. Optical scheme for sample treatment For different purposes of experiments, we have different treatment methods for your samples (cytosolic protein extraction, peripheral protein extraction or membrane protein extraction). Flowchart of the Pull Down Assay: Flowchart of the pull down assay Protocol for pull down assay (GST-tagged protein as an example) Construction of GST-tagged protein expression plasmid i. Choose proper expression vector according to the target protein
information provided by customers. ii. Insert the DNA sequence of target protein into the vector to generate recombinant expression plasmid. iii. Sequence the recombinant plasmid to assure no mutation in the sequence. iv. Transform the recombinant plasmid into E. coli component cell, and screen for positive clones. GST-fused protein expression and purification [1] i. coli BL21 for target protein expression. ii. Pick single colony into LB media with proper antibiotics, culture overnight. iii. Enlarge cultivation, to reach early exponential phase, add inducer to induce GST-fused protein expression (inducer free group as control). iv. Harvest bacterial cells, and resuspend with ice-cold cell lysis buffer. v. Pass the bacterial suspension through two freeze/thaw cycles. vi. Sonicate on ice to rupture bacterial cells and break up any DNA. vii. Add appropriate amount of DNase I and Triton X-100 into the cell lysate, incubate for 30 min at 4 °C with rotation. viii. Centrifuge the sample for 30 min at 4 °C. At the same time, treat the glutathione (GSH)-agarose beads with a small quantity of lysis buffer, centrifuge and carefully remove the supernatant. ix. Add the supernatant of lysate into pre-treated beads, incubate for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation. x. Centrifuge the mixture for 5 min at 4 °C, carefully decant the supernatant from the beads. xi. Rinse the beads with wash buffer, centrifuge for 5 min at 4 °C. Repeat for 3-4 times. xii. Add proper volume of bead storage buffer to the beads and store at -20 °C. The beads should never be allowed to freeze, or else the beads will crack. 50% glycerol can be added in the bead storage buffer to avoid this. xiii. Perform SDS-PAGE and stain with coomassie blue to analyze purification and quantitate the amount of protein bound to GSH beads (including inducer (+), inducer (-), supernatant, pellet, flow through, and beads sample). After positive colony verification, extract the plasmid and transform into E. Normalization of proteins bound to the beads is necessary when different GST fused proteins are used as bait proteins. Cross-linking of the target protein to beads i. proper size plastic column. Wash the column with PBS buffer twice. ii. Cross-link the GST fusion protein beads and column with cross-linker, incubate for 45 min at room temperature with continuous mixing. Add required volume of GST fusion protein beads to be cross-linked into
iii. Drain the column. iv. Add appropriate volume of quenching buffer to the column, gently mix for 10 min at room temperature (Block amine-reactive sites). v. Thoroughly wash the beads at 4 °C, store for use. Prepare GST fusion proteins and tissue lysate i. and store at -20 °C in bead storage buffer for up to 6 months. ii. Prepare a tissue lysate (choose lysis method suitable to different protein locations: cytosolic, peripheral, or membrane). Ensure that lysate is free from even small traces of particle contamination. Contamination will result in large amounts of nonspecific protein on the gel. If present, it is very important to remove them by high speed centrifugation. Prepare recombinant GST fusion proteins attached to GSH-agarose beads Pre-clear lysate with GSH beads i. GSH-agarose beads with wash buffer, centrifuge for 5 min at 4 °C, remove the supernatant and collect the beads in a minimal volume of buffer. ii. Combine the washed GSH beads with tissue lysate and incubate for 30 min at 4 °C. (Pre-clear the tissue lysate with the washed GSH beads for removal of endogenous GSTs present in the lysate and nonspecifically binding proteins) This will remove most of the endogenous cellular GST. iii. Collect the beads by centrifuge, and carefully pour off the supernatant into fresh, cooled tubes on ice. (Pre-cleared tissue lysate) iv. Repeat. This is especially important for tissue lysate that are rich in endogenous GSTs (particularly cytosolic extracts and lysates of specific tissues, for example, testis or liver). Wash a batch of (according to your sample amount) fresh or recycled Bind tissue lysate to the GST fusion protein beads