Organic vs Inorganic Compounds: 18 Basic Differences
50 likes | 106 Vues
Organic Compounds vs Inorganic Compounds - Find out here 18 major differences and other important factors. Know what is the difference between organic and inorganic chemicals.<br>

Organic vs Inorganic Compounds: 18 Basic Differences
E N D
Presentation Transcript
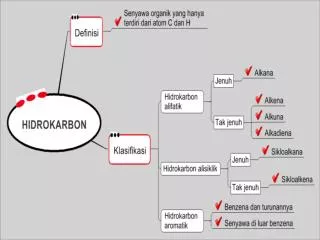
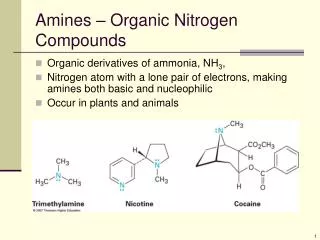
Chemistry is incomplete without learning about compounds. A compound is the combination of two or more different chemical elements that held together to form unbreakable chemical bonds. Two Categories of the Compounds: Organic Compounds Inorganic Compounds ● ● Read through the following to get detailed knowledge about these compounds. Let’s Explore Organic Compounds: These are the chemical compounds that are formed by carbon-hydrogen bonding. Organic compounds are extracted from living organisms like plants and animals. These compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth’s crust, but they are of great importance because every life is based on organic compounds. Some organic compounds are synthetically derived from petrochemicals like hydrocarbons, which are formed on their own from high pressure and temperature degradation of organic matter. Hydrocarbons, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins are the four significant examples of organic molecules that can form complex structures and long-chain elements. Although organic compounds are nonpolar molecules, thus they do not dissolve well in the water of the cell, but these do dissolve in other organic compounds in nature. Such four types of organic molecules – when it comes in contact with living tissues tend to form new compounds.
Let’s Leverage Inorganic Compounds: These are the chemical compounds that lack carbon-hydrogen bonds. However, there are no clear definitions that have clearly defined this factor. Inorganic compounds are mostly composed of the Earth’s crust. Most of the simple chemical compounds that contain carbon are often considered as inorganic. These compounds are contrastingly more colorful than organic compounds. Another factor that distinguishes it is its presence in the crust in crystal form. These have an adverse reaction on the human body if taken through the water supply. Some of the examples are Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide, Carbides, Cyanides, Cyanates, carbonates, and Thiocyanates. Nitrates, lead, copper, fluorides are also some of the examples of Inorganic Compounds. Organic Compounds vs. Inorganic Compounds The chemical compounds are of two major categories: i) Organic Compounds, ii) Inorganic Compounds. Even now, there is no specific description of what element falls under which category. There are a few very defining factors that explain the division of the elements under the two different categories. The commonly seen factor is that organic compounds are those who have carbon-hydrogen bonds, while other items that do have such bonding are classified as inorganic compounds, while there as some exceptions in this defining property. The significant characteristics which help to differentiate between organic and inorganic compounds are as follows: Basic Difference Between Organic & Inorganic Compounds No Organic Compounds Inorganic Compounds 1 They are found in all forms like gases, liquids or solids. They are mostly found in solid form. 2 It always contains carbon and forms carbon-hydrogen bonds. Some of them contain carbon but most of them contain metals and other elements. And it does not form carbon-hydrogen bonds.
3 They are obtained from living organisms, i.e., animals and plants. They are mostly extracted from non-living substances, i.e., minerals. 4 Organic compounds are biological. Inorganic Compounds are mineral in nature. 5 They form covalent bonds. They mostly form ionic bonds but there are exceptional cases of covalent bonding. 6 They are unable to make salts because of their tendency to form covalent bonds. They make salts. 7 They are composed of few elements only like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. They are all composed of well-known elements. 8 Some of the organic compounds are highly complex and have high molecular masses. Such complex compounds are stable. Inorganic compounds are less complex. And are comparatively less stable. 9 Organic compounds have low melting as well as boiling points. Inorganic compounds have higher melting and boiling points. 10 They are insoluble in water and are soluble in organic solvents. They are voluntarily soluble in water and are insoluble in organic solvents. 11 They are highly inflammable and volatile. They are not inflammable and non – volatile.
12 These compounds are poor heat and electricity conductors in aqueous solution. These compounds are good conductors of heat and electricity in aqueous solution. 13 They have a slower rate of reaction. They have a higher rate of reaction. 14 They produce a more complex set of products during the reaction. They produce a less complex set of products during the reaction. 15 They perform the phenomenon of isomerism. Only the coordination compounds show the isomerism phenomenon. 16 These include nucleic acids, fats, sugar, enzymes, proteins, and several fuels. These include salts, metals, and single element made substance and non-carbon and hydrogen-bonded compounds. 17 They are classified into many classes based on homologous series. Each class is represented by a general formula and the members show similar properties. They are classified into acids, bases, and salts. There is no homologous series in inorganic compounds. 18 Methane, ethane, acetylene, alcohols, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), urea [CO(NH2)2] are some examples of organic compounds. Carbon dioxide, sulphuric acid, NaCl, diamond (pure carbon) are some examples of inorganic compounds. Industrial Value of Inorganic Compounds Many companies across the world are synthesizing inorganic compounds like Ammonium Bisulphite, Sodium Sulphite, Sodium Bisulphite and Sodium Metabisulphite on a large scale. Have a glance at a brief description of these inorganic compounds.
Ammonium Bisulphite Solution It is a clear yellow colored solution that is free from foreign particles. It is used in oil fields and is used in manufacturing caramel food color. Sodium Sulphite Powder It is white colored clear crystalline powder which is mostly used in pharmaceutical companies and oil field industries. Sodium Bisulphite Solution It is a very clear and yellow-colored solution which is free from foreign particles. It is used as a de-chlorination agent in water treatment and is used as an oxygen scavenger in Oil Field Industries. Sodium Metabisulphite It is a free-flowing crystalline powder used for water treatment, photographic, mining, food, and medical industry. Sodium Bisulphite Powder It comes in the form of a white crystalline powder that is mostly used in chemical, pharmaceutical and water treatment industries. Moving Forward Shanti Inorgochem is one such company that is professionally working and producing inorganic compounds on an extremely large scale. It is a proficient company that produces both powdered and liquefied forms of Sodium Bisulphite in India.