Aggregate Planning and Scheduling
80 likes | 443 Vues
Aggregate Planning and Scheduling. Michael F. Gorman, Ph.D. MBA 691. Presentation Outline. Aggregate Planning – Long term: monthly, quarterly time periods for an annual or quarterly horizon Demand Variability: seasonality, monthly swings, lumpiness of orders

Aggregate Planning and Scheduling
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aggregate Planning and Scheduling Michael F. Gorman, Ph.D. MBA 691
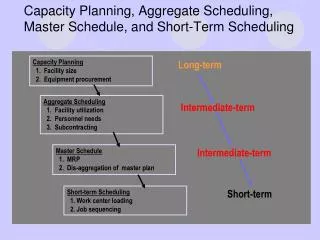
Presentation Outline • Aggregate Planning – • Long term: monthly, quarterly time periods for an annual or quarterly horizon • Demand Variability: seasonality, monthly swings, lumpiness of orders • Costs of Change: changing production levels is costly • Components of Aggregate Planning • Hiring/Firing • Overtime • Inventory • Scheduling • Detailed assignment of tasks, given a production plan • Assignment of tasks • Scheduling of shifts
Aggregate Planning • Basic facts: • Demand is typically not stable over time • It is inherently costly to change production levels • It is costly to carry inventory • Aggregate Planning balances the costs of changing production levels with the costs of carrying inventories • We explicitly model the costs of change over time. • Aggregate Planning is an “intertemporal” – between periods, or over time – model • Until now, we have looked at single-period models
Components of Aggregate Planning • Demand • Monthly, quarterly, annual • Varies over time • Production • A function of the number of workers, N, and the intensity of their work (regular time or overtime) • Inventory • It = It-1 + (Pt – Dt) • When Pt<>Dt, then inventory changes up or down • As Dt <> Dt-1 we have a number of options: (assuming Pt = Dt) • Dt > Dt-1: • Hire • Overtime workers • Pull from inventory • Create a backlog of orders (backorders) • Dt<Dt-1 • Fire • Reduce OT • Add to inventory • Reduce backlogs
Aggregate Planning Problem • Imagine you are planning the production plan for the next four months, given forecasted orders • Inputs: • Forecasted demand levels • Starting employment, inventory levels • Productivity (output per hour) • What is the cost-minimizing plan to meet these demands?
Job Assignment Problem • Given a number of different employees and a number of different jobs, what is the best assignment of jobs to employees? • Depends on who is best at what… • But what if one person is best at everything, or someone else is worse at everything? • How do you make the trade-offs? • Given a set of jobs that need to be completed, and a number of people that need to be completed, how should the jobs be assigned to minimize the cost (minimize the time) of completion?
Shift Scheduling Problem • Within-day and within-week demand patterns are variable, but people prefer or demand a regular work week. • Further, you often can’t call them in for one hour a day, or one day per week. • Given the constraints on work day and work week, what is the best shift schedule to minimize costs, given a demand pattern?