The Domain Name System
160 likes | 833 Vues
The Domain Name System Unix System Administration Download PowerPoint Presentation DNS’ History Mystery During the time of the dinosaurs (ARPANET) Single host file managed centrally and distributed to all hosts on the ARPANET Consumed lots ‘o bandwidth DNS Is Born

The Domain Name System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Domain Name System Unix System Administration Download PowerPoint Presentation
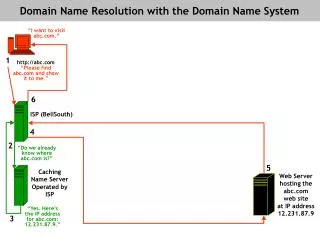
DNS’ History Mystery • During the time of the dinosaurs (ARPANET) • Single host file managed centrally and distributed to all hosts on the ARPANET • Consumed lots ‘o bandwidth • DNS Is Born • Original Unix work done by grad students at Berkeley, later managed by the ISC • Hierarchical, distributed database • Each site responsible for their portion of DNS
What’s In a Named? • DNS • Domain Name System • BIND • Berkeley Internet Name Domain system • named or in.named • Name of the BIND executable
Defining DNS Definitively • Hierarchical namespace for hosts and IP addresses • Host table implemented as a distributed database • “Resolver” or library routines for querying the database • Improved routing of email • Mechanism for finding services on the net • Protocol for exchanging naming info
DNS Goes Both Ways • Resolves names to IP addresses • Also resolves IP address to names (reverse DNS)
Vixie’s Various Versions • Paul Vixie was the major maintainer for BIND version 8 • Version 4 is still in use, but should be considered obsolete • Version 8 provides many advances that improved efficiency, security and robustness • Version 9 is a total rewrite and supports threads, multiprocessors IPv6 and more • There was no version 5, 6 or 7
What Kind of Bindage Are You Into? • Bind 4 used a config file called /etc/named.boot • Bind 8, 9 use /etc/named.conf • To determine if version 8 or 9 use: dig @server version.bind txt chaos e.g. dig @beast version.bind txt chaos
Masters, Slaves and the Authorities • Authoritative Servers • Master server (keeps official copy of zone info on disk) • Slave server (gets copy of zone info from master via zone transfer) • Cache Servers • Never authoritative • Load “root” domain servers but all others are accumulated in memory only
Binding Your Clients • Bind Client “Resolver” Configuration • /etc/resolv.conf • domain or search directives • nameserver directives (at most 3) • /etc/nsswitch.conf on some systems (like Solaris and Linux)
Putting Your Server In a Bind • /etc/named.conf • Zone files • See page 438 for record types
/etc/named.conf options { directory "/var/dns"; pid-file "/etc/named.pid"; fake-iquery yes; }; logging { category lame-servers { null; }; category cname { null; }; }; zone "." in { type hint; file "named.cache"; }; zone "0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" in { type master; file "named.local"; };
/etc/named.conf (continued) zone "91.159.in-addr.arpa" in { type master; file "tcnj.hosts.reversed"; }; zone "TCNJ.EDU" in { type master; file "tcnj.hosts"; }; zone "Trenton.EDU" in { type master; file "trenton.hosts"; };
@ IN SOA beast.TCNJ.EDU. admin.beast.TCNJ.EDU. ( 5923 ; serial number 10800 ; Refresh 3 hours 3600 ; Retry 1 hour 604800 ; Expire 168 hours/1 week 43200 ) ; Minimum 12 hour IN NS beast.TCNJ.EDU. IN NS seuss.TCNJ.EDU. IN NS snuffy.TCNJ.EDU. localhost 43200 IN A 127.0.0.1 beast IN A 159.91.15.220 beast IN MX 20 beast.TCNJ.EDU. TCNJ.EDU. IN MX 20 beast.TCNJ.EDU. lion IN A 159.91.15.221 lion IN MX 20 beast.TCNJ.EDU. tsclion IN CNAME lion.TCNJ.EDU. sa.tcnj.edu. IN NS cartman.sa.tcnj.edu. cartman.sa.tcnj.edu. IN A 159.91.8.228
91.159.in-addr.arpa. IN SOA beast.TCNJ.EDU. ssivy.beast.TCNJ.EDU. ( 5774 ; serial number 10800 ; Refresh 3 hours 3600 ; Retry 1 hour 604800 ; Expire 168 hours/1 week 43200 ) ; Minimum 12 hour IN NS beast.Trenton.EDU. IN NS snuffy.Trenton.EDU. IN NS seuss.Trenton.EDU. localhost 43200 IN A 127.0.0.1 220.15.91.159.IN-ADDR.ARPA. PTR beast.TCNJ.EDU. 221.15.91.159.IN-ADDR.ARPA. PTR lion.TCNJ.EDU. 228.8.91.159.IN-ADDR.ARPA. cartman.sa.tcnj.edu.
@ IN SOA beast.trenton.edu. admin.beast.tcnj.edu. ( 3 ; Serial number 10800 ; Refresh rate in seconds for secondary servers 3600 ; Retry in seconds after failure 3600000 ; Expire in seconds 86400) ; Default time-to-live in seconds IN NS beast.tcnj.edu. 1 IN PTR localhost.
Root Name Servers . 3600000 IN NS A.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. A.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 198.41.0.4 . 3600000 NS B.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. B.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 128.9.0.107 . 3600000 NS C.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. C.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 192.33.4.12 . 3600000 NS D.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. D.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 128.8.10.90 . 3600000 NS E.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. E.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 192.203.230.10 . 3600000 NS F.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. F.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 192.5.5.241 <… blah, blah, blah …> . 3600000 NS M.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. M.ROOT-SERVERS.NET. 3600000 A 202.12.27.33