Mastering Exponential Functions in Aeronautical Controls
110 likes | 163 Vues
Explore exponential functions in aeronautical controls, understanding exponential rate variations and their applications in aerobatics. Learn the general formula and typical graphs of exponential functions, as well as solving exponential equations, simple and compound interest, and continuous compounding. Discover the impact of compounding periods on financial outcomes, while also delving into the irrational number e. Complete engaging exercises for a comprehensive grasp of the material.

Mastering Exponential Functions in Aeronautical Controls
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Exponential Functions Lesson 2.4
Aeronautical Controls • Exponential Rate • Offers servo travel that is not directly proportional to stick travel. • Control response is milder below half-stick, but becomes increasing stronger as stick travel approaches 100%. Great for aerobatics and trouble situations. What airplane is this?
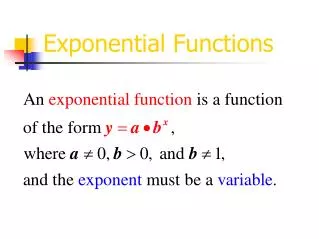
General Formula • All exponential functions have the general format: • Where • A = initial value • B = growth rate • t = number of time periods
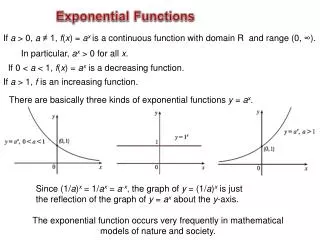
Typical Exponential Graphs • When B > 1 • When B < 1
Exponential Equations • Given • What could you say about x and y? • If the two quantities are equal and the base value for the exponential expression are the same . . . • Then the exponents must be the same • Use to solve exponential equations
Simple Interest • If you start with an amount P, the principal • and receive interest rate at r% • for time t • Then the interest earned is I, the product of P, r (as a decimal) and t
Compound Interest • Consider an amount A0 of money deposited in an account • Pays annual rate of interest r percent • Compounded m times per year • Stays in the account t years • Then the resulting balance At
Compound Interest • What happens when we increase the number of compounding periods? • Try $1000 at 3.5% for 6 years • Compounded yearly? • Quarterly • Monthly • Weekly • Daily • For every hour? every minute? every second?
The Irrational Number e • As the number of compounding periods increase • The change in the end result becomes less • We reach a limit • Can be shown • Where e ≈ 2.71828 • Note Page 90, 91
Continuous Compounding • Try our $1000 at 3.5% for 6 years using • Compare to with large m
Assignment • Lesson 2.4 • Page 106 • Exercises 3 – 47 EOO