Unit 3 –The Water Cycle Lesson 1
601 likes | 852 Vues
Unit 3 –The Water Cycle Lesson 1. California State Standards. 3.a – Students know most of Earth’s water is present as salt water in the oceans, which cover most of Earth’s surface.

Unit 3 –The Water Cycle Lesson 1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
California State Standards • 3.a – Students know most of Earth’s water is present as salt water in the oceans, which cover most of Earth’s surface. • 3.b – Students know when liquid water evaporates, it turns into water vapor in the air and can reappear as liquid when cooled or as a solid if cooled below the freezing point of water. • 3.c – Students know water vapor in the air moves from one place to another and can form fog or clouds, which are tiny droplets of water or ice, and can fall to Earth as rain, hail, sleet or snow.
McWay Falls, CA Where did the water in the waterfall come from? Where does water in rivers come from and where does it go? How is the water in the waterfall different from ocean water?
Vocabulary Terms • water cycle- the constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to Earth’s surface.
Vocabulary Terms • water vapor– the gas form of water.
Vocabulary Terms • water vapor– the gas form of water. • Vapor is another way of saying gas.
Vocabulary Terms • water vapor– the gas form of water. • evaporation – the process by which a liquid changes into a gas.
Vocabulary Terms • water vapor– the gas form of water. • evaporation – the process by which a liquid changes into a gas. • These two terms both have to do with a gas.
Vocabulary Terms • condensation – the process by which a gas changes into a liquid.
Vocabulary Terms • condensation – the process by which a gas changes into a liquid. • What does dense mean?
Vocabulary Terms • condensation – the process by which a gas changes into a liquid. • What does dense mean? • Dense means thick. Condensation is the process in Which a gas becomes denser and forms a liquid.
The Water Planet BIG IDEA: Water covers almost three-fourths of Earth’s surface!
The Water Planet • Water covers almost three-fourths of Earth’s surface. • A little more than 97% of Earth’s water is found in the oceans. • Ocean water is salty. • Saltwater can also be found in some lakes. • California’s Salton Sea is a saltwater lake.
The Water Planet • The rest of the Earth’s water is fresh water. • Fresh water is water with very little salt. • Less than 3% of all Earth’s water is fresh water. • Most of the fresh water on Earth is frozen in ice caps and glaciers.
The Water Planet • Most of the remaining fresh water can be found underground. • Underground water is the only source of fresh water for many people around the world. • Only .5% of all the fresh water on Earth is found in the air, soil, rivers, and freshwater lakes.
Review Time • What percentage of water on Earth is salt water?
Review Time • What percentage of water on Earth is salt water? 97% of water on Earth is salt water.
Review Time • Where is most of the fresh water on Earth found?
Review Time • Where is most of the fresh water on Earth found? Most of the fresh water on Earth is found frozen in glaciers and ice caps.
Review Time • List three places where liquid fresh water can be found.
Review Time • List three places where liquid fresh water can be found. • Underground • In lakes • In rivers • In soil • In the air
Summarize • Summarize where water can be found on Earth.
Summarize • Summarize where water can be found on Earth. • Most of Earth’s water is present as salt water in the oceans. Most of the rest of Earth’s water is frozen in glaciers.
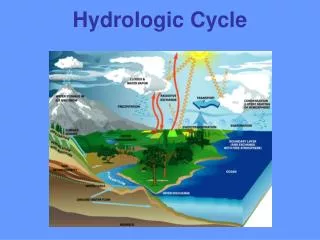
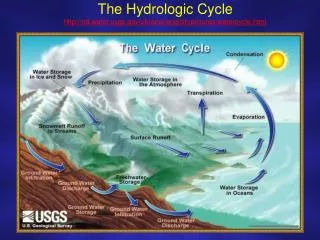
The Water Cycle BIG IDEA: Water moves constantly throughout our environment.
The Water Cycle • Water moves constantly throughout the environment. • The water cycle is also known as the hydrologic cycle. Air Earth’s surface
The Water Cycle • How does it work? • Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. • The sun’s energy warms water on the Earth’s surface. • This causes some of the water to turn from a liquid to a gas.
The Water Cycle • How does it work? • Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. • The sun’s energy warms water on the Earth’s surface. • This causes some of the water to turn from a liquid to a gas. What is the gaseous form of water called?
The Water Cycle • How does it work? • Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. • The sun’s energy warms water on the Earth’s surface. • This causes some of the water to turn from a liquid to a gas. What is the gaseous form of water called? WATER VAPOR
The Water Cycle • How does it work? • Energy from the sun drives the water cycle. • The sun’s energy warms water on the Earth’s surface. • This causes some of the water to turn from a liquid to a gas. • The water vapor moves into the air. • When water vapor cools, it becomes a liquid again. • Once it becomes heavy enough, it falls back to Earth
The Water Cycle • Water may fall back into the ocean, lakes, rivers, or onto the ground. • When it falls on land, it can be soaked into the ground, or run off the surface into rivers and lakes.
The Water Cycle • Water may fall back into the ocean, lakes, rivers, or onto the ground. • When it falls on land, it can be soaked into the ground, or run off the surface into rivers and lakes. Think back to yesterday’s picture of the waterfall. Where did some of the water in the waterfall come from?
The Water Cycle • Water may fall back into the ocean, lakes, rivers, or onto the ground. • When it falls on land, it can be soaked into the ground, or run off the surface into rivers and lakes. • Some water can quickly recycle back to the atmosphere if the sun heats it and it it turns into water vapor again. THIS IS HOW THE WATER CYCLE CONTINUES!
The Water Cycle • Most of the water moving through the water cycle comes from the oceans. • The sun’s energy heats water on the oceans’ surface, and turns it into water vapor. • Winds carry the water vapor over land, where it becomes liquid water. • It falls as rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
The Water Cycle • Most rainwater comes from the oceans. • When water from the oceans turns into water vapor, all of the salt that had dissolved in the water stays in the ocean. • When the water vapor cools, fresh water forms and falls to Earth.
Why are oceans salty? • Water drops begin to fall to Earth, some fall on land. • These drops dissolve small amounts of salts and minerals on the land. • The water with the salt and minerals runs off into the rivers. • The rivers carry the water to the oceans. • Over time the salts build up in the ocean.
Let’s Get Visual! • Open your textbooks to pages 228-229. • In your table rows please do the following: • Look at the “Science Close Up” diagram. • Read the captions together in your groups. • What is the diagram trying to show you?
The Water Cycle Song! The Water Cycle Song
Review Time • How does water on Earth’s surface enter the air?
Review Time • How does water on Earth’s surface enter the air? Heat causes it to change to a gas from a liquid. As a gas, water rises into the air.
Review Time • What energy source drives the water cycle?
Review Time • What energy source drives the water cycle?
Review Time • How does salt water become fresh water?
Review Time • How does salt water become fresh water? When salt water in the ocean becomes water vapor, salt is left behind in the ocean. The water vapor is fresh water.
The Water Cycle Evaporation
Evaporation • Evaporation is the process by which a liquid changes into a gas. • Water evaporates because heat changes it from a liquid to a gas, also called water vapor. • It is hard to see evaporation because water vapor is invisible. • We can infer water has evaporated when it seems to disappear, like a puddle disappearing from on the ground.
Evaporation • A large amount of water evaporates from Earth’s oceans, lakes, and rivers every day. • Water also evaporates from the soil, from puddles, from plants, and even your own skin! • As water evaporates, is goes up into the air and mixes with other gases. • Water vapors become part of the air. • When the wind blows, the air moves along with the water vapors.
The Water Cycle Condensation
Condensation • When water vapor becomes part of the air, it moves with the air. • Air can carry water vapor very long distances. • It can also carry water vapor high into the atmosphere. • Changes in the air temperature affect the water vapor. • As air and water vapor move up, they cool. • When they get cold enough, condensation occurs.
Condensation • Condensation is the process by which a gas changes into a liquid. • Air has dust particles in it. • When water vapor condenses, it changes into a liquid on the dust particles. • The water vapor and dust form clouds and fog.