River Erosion and Deposition
110 likes | 445 Vues
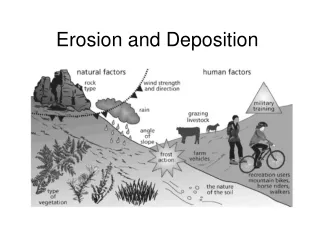
River Erosion and Deposition. Rivers Shape the Land. Even the smallest stream has the ability to pick up objects Erosion is the process by which fragments of soil and rock are broken off from the ground surface and carried away.

River Erosion and Deposition
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Rivers Shape the Land • Even the smallest stream has the ability to pick up objects • Erosion is the process by which fragments of soil and rock are broken off from the ground surface and carried away. • These fragments are carried away until they are eventually dropped off or deposited in a new location
Rivers Shape the Land • Deposition is the process by which soil and rock are left behind • Rivers wear away land forms through erosion and build new landforms through deposition • Particles that are picked up and dropped off by moving water are called sediment. • Sediment that has not been dropped off is called a suspended load.
Rate of Erosion/Deposition • A river’s speed affects its ability to wear away or erode the land • Faster speed = more energy • Slower speed = less energy • The more energy a river has the heavier the sediments it can move. • As a river slows it drops the heavier sediments first.
What affects the speed of a river? • Steepness of its slope • Volume of water in the river • Increase in water = increase in speed • Shape of the river channel • As the water rubs against the sides and bottom it creates friction • In a narrow and shallow channel there is more friction so the water flows slowly
What affects the speed of a river? • Friction between the water molecules and sides and bottom of river cause the water to move slower • The velocity of a stream is the greatest away from the bottom and sides • On the outside of curves
Parts of a River • Headwaters- small streams that come together at the source of a river • Flood Plain • River created valley by erosion • Small obstacle cause a bend in the river • River flows faster on the outer edge of the curve causing erosion • River deposits sediment on the inner curve
Parts of a River • The process of erosion and deposition creates a looping curve known as a meander. • Eventually the river may break through the meander and create a new channel. • The crescent shaped, cutoff body of water is called an oxbow lake. • Mouth– the point where a river flows into another body of water
Parts of a River • As the river’s water reaches the larger body of water the speed of the rivers slows. • This causes sediments to deposit at the mouth of the river • The deposits build up forming what’s called a delta.
River Erosion ABC Write • Is a river more likely to erode the land around its headwaters or at its mouth? Why?