THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
270 likes | 751 Vues
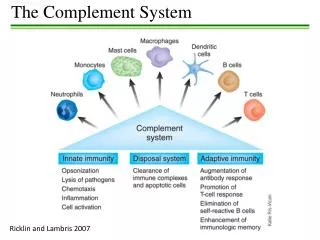
THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM. Help!. COMPLEMENT. A group of sequentially reacting proteins, which upon activation, mediate a number of biological reactions important to host defense. COMPLEMENT NOMENCLATURE. “C” - designation for 11 of the complement proteins (C1, C2, etc.)

THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
E N D
Presentation Transcript
COMPLEMENT A group of sequentially reacting proteins, which upon activation, mediate a number of biological reactions important to host defense
COMPLEMENT NOMENCLATURE • “C” - designation for 11 of the complement proteins (C1, C2, etc.) • Factor - designation for many alternative pathway components (factor B) • Overbar - indicates an enzymatically active protein or complex • Lower case letters - indicates a proteolytic cleavage fragment (C3a or C5a) • “R” - designation for receptors in the complement system (CR1 or C5aR)
Proteins of the Complement System Activation Regulation Receptors C1q, C1r, C1s, C2 - C9, Factors B & D, MBP, MASP-1-3, sMAP, ficolin C1-INH, C4BP, factors H and I, S protein, Sp-40,40 Serum Soluble Membrane Bound CR1 - CR4 C3aR, C5aR, CRIg, C1qR CR1, CD59, DAF, MCP
Modular Structure of Complement Proteins • Enzymes - (Serine Protease Domain) • C1s, C1r, C2, factors B, D and I • Collectins - (Collagen Stalk, Gobular Domain) • C1q, MBP and Ficolin • Cytolytic – (MACPF/CDC superfamily) • C6, C7, C8 and C9 • Regulatory and Receptor (SCR Domain) • DAF, MCP, C4BP, CR1, CR2 and factor H • “True” Complement Proteins • C3, C4 and C5
Complement Biosynthetic Sites • Hepatocytes • Monocyte/Macrophage • Hematopoietic • Fibroblasts • Endothelial • Reproductive • Adipocytes • Astrocytes • Neurons
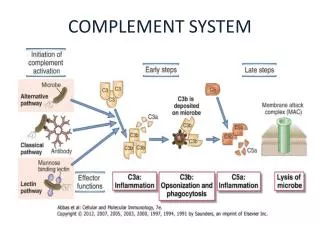
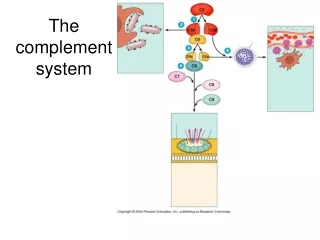
COMPLEMENT PATHWAYS MASP-1 CLASSICAL MBP/Ficolin ALTERNATIVE Properdin C3 C3a C3b C5 C5a C5b + C6-C9 TERMINAL
Chemotaxis Inflammation Opsonization Neutralization B cell activation Chemotaxis Inflammation Lytic complex formation Complement Host Defense Functions C3a C3 C3b C5a C5 C5b
Complement Activation • Classical Pathway - Ag-Ab complexes • Mannan-Binding Protein Pathway - Mannose, N-acetylglucosamine • Alternative Pathway - LPS, zymosan
C1q and C1 Structure C1=C1q,C1s2,C1r2 C1q C1s C1r
C3a/C5a Biological Functions • Anaphylatoxic and Chemotactic molecules • Degranulation of mast cells, basophils and eosinophils (histamine release) • Induce increased vascular permeability, edema • Induce cytokine release, adhesion molecule and acute phase protein expression • Induces/augments respiratory burst
C5b Biological Functions • Initiation of the membrane attack complex: the nonproteolytic association of C5b, C6, C7, C8 and C9 leading to the formation of a membranolytic pore-forming complex • Signal transduction for numerous cellular events
C3b Biological Functions • Opsonization of Ag-Ab complexes for clearance • Solubilization of immune complexes • Neutralization of invading pathogens
COMPLEMENT REGULATION CLASSICAL MBP ALTERNATIVE C3 C3a C3b C5 C5a C5b + C6-C9 TERMINAL
COMPLEMENT REGULATION • Regulation is in proportion to the amount of activator • Limited half-life for the convertases, through regulatory proteins • Inhibitory proteins to control early activation • Carboxypeptidases to inactivate the anaphylatoxins • Inhibitory proteins to modulate MAC formation
C3b factor B Bb C3b C3b Bb Regulation of Complement Activation DAF Inhibition Decay Acceleration DAF
C5b-8 C9 Regulation of Complement Activation (Terminal Pathway) Inhibition ofC9binding CD59
Complement Deficiencies & Treatment Options • Activation Components - recurrent bacterial infections - antibiotics, replacement therapy? (C2, factors B and D, MBP and properdin deficiencies) • SLE (C1 and C4 deficiencies) • Terminal Components - recurrent bacterial infections - antibiotics, replacement therapy? (C5-C9 deficiencies)
Complement Deficiencies & Treatment Options • Regulatory Components • HANE (C1-INH deficiency) – replacement therapy, kallikrein inhibitors • PNH (DAF, CD59 deficiency) – anti-C5 Ab • aHUS (CD46 deficiency) • Receptors – SLE (low CR1 expression), life-threatening bacterial infections (CR3, CR4 deficiencies) – bone marrow transplantation