How to solve an equation in one variable?
60 likes | 227 Vues
How to solve an equation in one variable?. If the EQ has radicals and the unknown is in one radicand, isolate that radical and get ride of it by powering the reciprocal of its index of the radical on both sides of the equation.

How to solve an equation in one variable?
E N D
Presentation Transcript
How to solve an equation in one variable? • If the EQ has radicals and the unknown is in one radicand, isolate that radical and get ride of it by powering the reciprocal of its index of the radical on both sides of the equation. • If the EQ has absolute values and the unknown is inside of one of them, isolate it and unfold the equation as two linear equations using “|x|=a for a>0 is equivalent to x= a or x=-a”. • If the EQ has fractions, eliminate the denominators by multiplying its LCD onboth sides of the equation. • If the EQ has parenthesis and the unknown is inside of one of them remove parenthesis using the distributive law. • Combining like terms on each side of the equation. • If it is Linear Equation • regroups terms with the unknown on the left side of the equation and the rest on the right side. • If it is a Quadratic Equation • write the EQ in the standard form ax2+ bx +c = 0 and solve using either factoring method or using thequadraticformula.
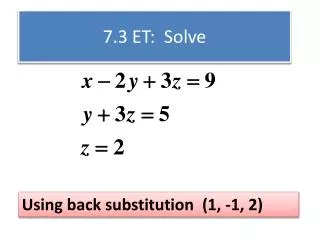
Equation Involving radicals Ex 1: Solve the equation for x: Sol: Isolate the radical term to left side: Squaring both sides: Expand and simplify: Factor: By Zero-Factor Property: Check: When x = 1: When x=6: Therefore, x = 6 is the only solution. Return to Table
Equation Containing Absolute Values. Ex 2: Solve the equation for x: Sol: Isolate the absolute value term to one side: Remove the absolute value sign and solve the following two equations: Group the x-terms to left side and solving for x: Check: When x = 6: When x= ½: Thus X = 6 & x = ½ are two solutions. Return to Table
Return to Table Equations Containing Fractions Ex 3:Solve the equation for x: Sol: Multiply both sides by the LCD=20: Use the distributive law on left side: Simplify on both sides: Add 14 to both sides: Divide each side by 12: Check: Return to Table Thus x=19/12 is the solution.
Equations Involving Parenthesis Ex 4: Solve the equation for x: Sol: Use the distributive law to remove the parenthesis: Simplify each side: Isolate the x-terms to left side: Simplify each side: Divide each side by 17: Check: Thus x = 2 is the solution. Return to Table