The Rock Cycle
180 likes | 375 Vues
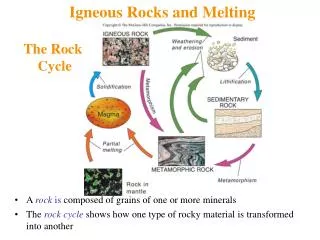
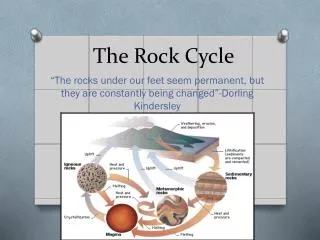
The Rock Cycle. Thinking about relationships among the major rock groups. Major Rock Groups. Igneous Formed from a magma (molten rock) either erupting onto the surface or being held below the surface and cooling. Sedimentary

The Rock Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Rock Cycle Thinking about relationships among the major rock groups
Major Rock Groups • Igneous • Formed from a magma (molten rock) either erupting onto the surface or being held below the surface and cooling. • Sedimentary • Formed from sediments such as mud, sand and gravel that accumulate in layers on the floor of places like the sea, lakes or river deltas. These sediments have been compacted and often cemented together to form rocks • Metamorphic • formed beneath the surface when older igneous and sedimentary rocks are transformed by a combination of heat and pressure.
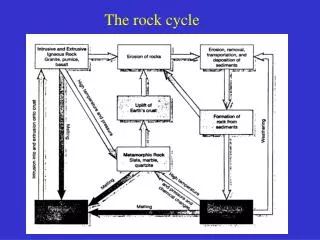
Fig. 2.9 MAGMA
IGNEOUS Crystallization MAGMA
IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization MAGMA
Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization MAGMA
Weathering Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
SEDIMENT SEDIMENT Weathering Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
What is Weathering & Erosion? • Weathering is the breaking down of rocks by natural processes. Weathering can break rocks down in three different ways, described as physical weathering, chemical weathering and biological weathering. • Erosion is the movement of soil and other weathered material from one place to another. It can be done by wind or water, and the water can be moving quickly like a river, repetitively like the sea or slowly like a glacier.
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Burial Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Can you see any shortcuts? SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA
In Conclusion… • The rock cycle demonstrates the relationships among the three major rock groups • It is powered by the interior heat of the Earth • As well as earth’s momentum and… • The energy from the sun • It involves processes on the Earth’s surface as well as the Earth’s interior • It connects the “hydrologic cycle” with the “tectonic cycle”.
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA
Tasks to complete • Draw a simple diagram of the Rock Cycle • Write a paragraph to explain what the diagram shows. Include the processes linking each type of rock • Erosion and weathering are two processes that are easily confused. Explain what each process does