FASTENERS
320 likes | 1.19k Vues
FASTENERS. FASTENERS. Fasteners Described by several factors: Material Head style Type Diameter Length Thread count. FASTENERS. Material Describes what the fastener is made from Some common examples: Stainless steel Steel Brass

FASTENERS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FASTENERS • Fasteners • Described by several factors: • Material • Head style • Type • Diameter • Length • Thread count
FASTENERS • Material • Describes what the fastener is made from • Some common examples: • Stainless steel • Steel • Brass • Special coatings may also be added, such as zinc, in order to prevent corrosion or enhance appearance
FASTENERS • Head style • Describes the type of head on the fastener • Selected depending upon the purpose of the fastener • Common head styles: • Flat • Oval • Pan • Truss • Round • Hex
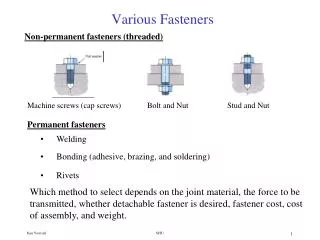
FASTENERS • Type • Designates the purpose of the fastener • Some common types: • Wood screw • Machine screw • Sheet metal screw • Self drilling or self tapping • Hex bolt • Carriage bolt • Lag bolt • Set screw
FASTENERS • Diameter is expressed in inches with the exception of small screws • Expressed as a size number preceded by the # sign (i.e. #12) • Differing size numbers correspond with fractional measurements • A complete chart can be found in most handy reference guides
FASTENERS • Sample chart:
FASTENERS • Diameter is normally measured as shank diameter except in the case of tapered screws, such as wood screws, where the root is measured instead • Length is normally expressed in inches and is measured from where the material surface is assumed to be (the end of the fastener) • If the fastener head sits above the surface, the measurement is measured directly under the head of the fastener
FASTENERS • If the fastener is designed to be countersunk, the measurement is made from the point on the head where the surface of the material is • Thread count • Expressed as Threads Per Inch (TPI) • Simply means the number of threads per inch measured along the length of the fastener • Used only with American fasteners • Only applies to machine threads • In general, smaller fasteners have finer threads, therefore the thread count will be higher
FASTENERS • The relationship between a fastener size (diameter) and the number of threads per inch is standardized in a series • Two most common United States thread series: • UNC (or NC) – Unified Course Thread (commonly called course) • UNF (or NF)– Unified Fine Thread (commonly called fine) • A complete table for these series can be found in most handy reference guides
FASTENERS • Sample table:
FASTENERS • Bolt grade • One final factor that should be considered when dealing with bolts is grade • Bolt grade is designated by numbers on the bolt head • The following are common grades of bolts: • Grade 2 • Steel • Most common • Least expensive • Have no head markings
FASTENERS • Grade 5 • Case hardened steel (outside only is hardened) • Not as strong as a fully hardened bolt • Designated by three evenly spaced radial lines on the head • Grade 8 • Fully hardened steel • Very hard but somewhat brittle • More likely to snap off rather than bend under extreme load • Designated by 6 evenly spaced radial lines
FASTENERS • Alloy steel • High strength steel alloy • Heat treated • Typically not plated resulting in a dull black finish • Extremely strong, but very brittle • It is important to have all physical factors (especially thread count) or the fastener will not fit properly • This also applies to any corresponding nut
FASTENERS • Metric fasteners • Described similarly to American fasteners (material, head style, type) • Use thread pitch rather than thread count • Thread pitch • Distance between threads • Expressed in millimeters (measured along the length of the fastener) • Example: a thread pitch of 1.5 means that the distance between one thread and the next is 1.5mm
FASTENERS • Different thread pitch designations similar to American fasteners: • Standard • Fine • Extra or super fine • Nuts and washers • Fasteners have numerous accessories to accompany them and it is just as important to replace these items at the same time
FASTENERS • The following are common nuts and their uses: • Hex nut • Nylon insert lock nut • Has a nylon insert to prevent backing off • Also referred to as a Nylock • Jam nut • Hex nut with reduced height • Wing nut • Has wings for hand tightening • Cap or Acorn nut • Has a domed top over the end of the fastener
FASTENERS • Flange nut • A nut with a built in washer • Kep nut • A nut with a built in external tooth lock washer • Used to speed up assembly • Square nut • Prevailing torque lock nut • Non-reversable • Used for high-temperature applications
FASTENERS • The following are common washer types and their uses: • Flat • Used to distribute load • Fender • Oversized flat washer • Better distributes load especially on soft materials • Finishing • Used for a finished appearance • Used with oval head screws • Split lock • Most common style • Used to prevent nuts and bolts from backing out
FASTENERS • External tooth lock • Used to prevent nuts and bolts from backing out • Internal tooth washer • Identical to above except teeth are inside