Structure of RNA
240 likes | 2k Vues
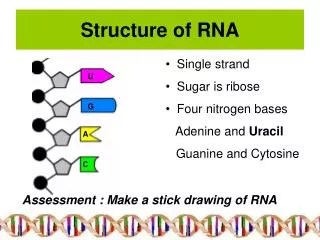
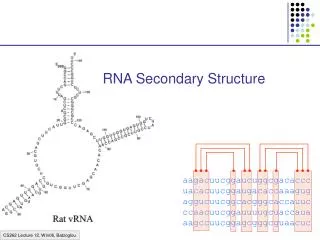
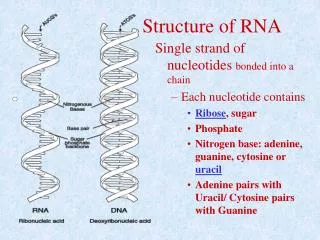
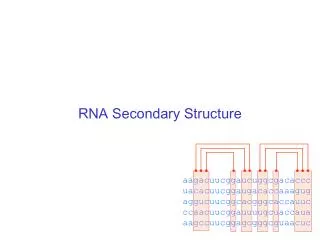
U. G. A. C. Structure of RNA. Single strand Sugar is ribose Four nitrogen bases Adenine and Uracil Guanine and Cytosine. Assessment : Make a stick drawing of RNA. Assessment: Tabulate the Differences between DNA and RNA. Three types of RNA and their functions.

Structure of RNA
E N D
Presentation Transcript
U G A C Structure of RNA • Single strand • Sugar is ribose • Four nitrogen bases • Adenine and Uracil • Guanine and Cytosine Assessment : Make a stick drawing of RNA
Three types of RNA and their functions • 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) which acts as a template for protein synthesis and has the same sequence of bases as the DNA strand that has the gene sequence. 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
2. Transfer RNA (tRNA), one for each triplet codon that codes for a pecific amino-acid (the building blocks of proteins). tRNA molecules are covalently attached to the corresponding amino-acid at one end, and at the other end they have a triplet sequence (called the anti-codon) that is complementary to the triplet codon on the mRNA. 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) which make up an integral part of the ribosome, the protein synthesis machinery in the cell.