South Asia Box Notes
330 likes | 450 Vues
This unit examines the profound effects of tectonic forces and monsoonal weather patterns on South Asia's physical geography, economy, and population. It highlights notable elements such as the Himalayas as natural borders, the Deccan Plateau's challenging terrain, and the significant river systems including the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra. Furthermore, it addresses environmental issues, rapid population growth, cultural factors, and the effects of cyclical weather phenomena like monsoons and cyclones. Understanding these aspects is crucial for sustainable development in the region.

South Asia Box Notes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
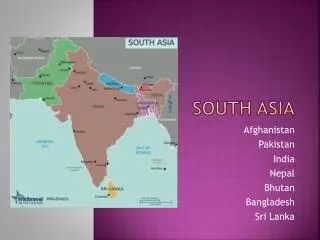
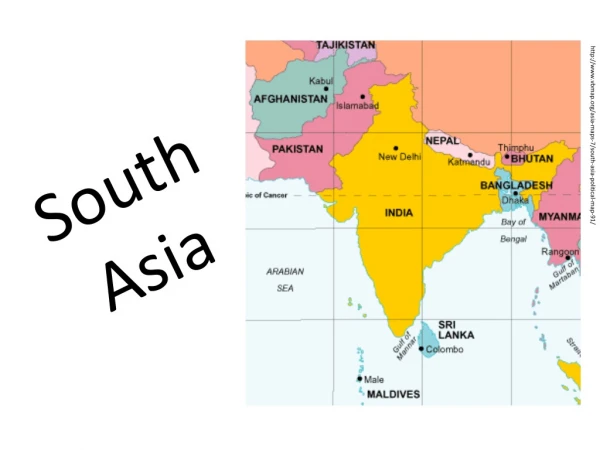
South Asia Box Notes Unit 10
Box #1: Physical Geography Elements Impact of Tectonic Forces in South Asia • Lithosphere – Mountains as a natural border • Northern part of subcontinent • Western & Eastern Ghats • Landlocked: Nepal & Bhutan • Deccan Plateau – Rugged landforms make settlement difficult • Maldives – archipelago • 3 Rivers: Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra Key Terms • Subcontinent • Alluvial plain • Deposition • Archipelago • Vegetation • Estuary • Delta • Renewable resource
Box #2: Weather & Environmental Drama Elements of Drama • Climatic Factors • LEMPOS (wet/dry season) • Many river systems cause massive flooding in low lying areas (good & bad results) • Cultural changes due to physical environment • Ways to adapt to flooding • Importance of renewable resources • Sustainable development is essential Key Terms • Monsoon • Summer monsoon • Winter monsoon • Cyclone • Tsunami • Storm surge • Adapt • Modify
Wet Monsoon: May-September Dry Monsoon: October-Apri
Effects of the monsoon - Some parts of India get an average of 100 in. of rain per year. - (Dallas only gets 35 in.)
Cyclones • Rapid inward curculation of air masses about a low pressure center • Hurricanes, cyclones, and typhoons are all the same weather phenomenon
Bangladesh and cyclones • Due to its location, Bangladesh suffers from cylones frequently. • The funnel-shaped northern portion of the Bay of Bengal and river deltas on the coast of the country combine for cyclones to be very damaging
Box #3: Economic & Population Issues Cultural Factors • Rapid population growth • Environmental consequences: pollution, flooding, unsanitary water, deforestation, strain on natural resources • Human consequences: overcrowding, crowded urban centers, spatial inequality, lack of infrastructure (providing services such as healthcare), cultural diffusion • Population density: cities near water (NE/SW) as mountains and Deccan Plateau get in the way of settlement • Steady population growth, longer life expectancies, and a drop in infant mortality rate have caused issues • Effects of an aging population: Aging populations require plans for healthcare and income in old age • Workforce in India will remain stable due to continued growth and improvement in education for women (a literacy gap between literacy men & women remains) • Balance of trade (comparing net imports vs. net exports) = A country with balanced trade will have equal amounts, or more exports than imports and economic growth • Can be influenced by a country’s physical geography (landlocked, islands) • Countries with certain physical features have negative trade balances: Islands, Archipelagos, Landlocked; Nepal has the worst balance of trade Key Terms • Infrastructure • Spatial inequality • Infant mortality rate • Cross-culturalization • Urban • Import • Export • Arable land • Entrepreneur • Sustainable Development
Activity • Create a population pyramid for India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka with the information provided
Box #4: Human Geography Elements Cultural Factors • Domination of Religions in Region: Hinduism, Buddhism, & Sikhism • Caste System – Hindu practice outlawed in 1947 • Diffused throughout subcontinent • Importance of Gandhi and his nonviolent resistance movement • Born into a caste, reincarnation to move • Kashmir Region: Hindu Kush Mountains – Primarily Muslim region controlled by Hindu dominated India Key Terms • Polytheism • Caste system • Constitutional monarchy • Raj • Cultural convergence • Cultural divergence • Nonviolent resistance • Gandhi • Kashmir