One Dimensional Kinematics
250 likes | 504 Vues
One Dimensional Kinematics. What is a Measurement?. A measurement is a comparison between an unknown quantity and a standard. Measurements quantify observations. Careful measurements enable you to derive the relation between any two quantities. Section. SI Units. 1.1.

One Dimensional Kinematics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a Measurement? • A measurement is a comparison between an unknown quantity and a standard. • Measurements quantify observations. • Careful measurements enable you to derive the relation between any two quantities.
Section SI Units 1.1 The Système International d’Unités, or SI, uses seven base quantities, which are shown in the table below.
Section Fundamental Units 1.1 SI Units The base quantities were originally defined in terms of direct measurements.
Derived Units Other units, called derived units, are created by combining the base units in various ways.
An example of a derived unit In the metric system force is measured in Newtons 1Newton = 1 kg m/s2 What does this quarter pounder with cheese have to do with the Newton?!
Derived Unit Example (cont) In the metric system the unit of energy is the Joule (pronounced JOOL). 1 Joule = 1 kg m2/s2
The standard for length the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1/299,792,458 of a second
The standard for time… One second is the time for radiation from a cesium-133 atom to complete 9,192,631,770 oscillation cycles.
The standard for mass is… One kilogram is the mass of a particular platinum-iridium cylinder kept at the International Bureau of Weights and Standards, Sèvres, France.
Modeling Activity Create a flip book showing a car that is • moving at the same speed, OR • Slowing down, OR • Speeding up
3 types of motion • Translational Motion Motion along a line.
2.Circular Motion Motion in a circle or in a plane.
3. Rotational Motion The motion of objects that move along a line and circle simultaneously. Example: Walking
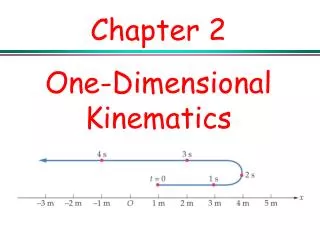
Motion Diagrams An easy way to study motion is to make a “movie” of a moving object. A motion diagram represents an object’s motion at several equally spaced instants of time
Particle Model A simplified version of a motion diagram
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION The study of motion along one axis without rotation
Which car is going faster, 1 or 2? Assume there are equal intervals of time between the frames of both movies. Car 1 Car 2
Which car is going faster, 1 or 2? Assume there are equal intervals of time between the frames of both movies. Car 1 Car 2 2 is going faster