Reactive Chemistry of Carboxylic Acids and Esters
130 likes | 173 Vues
Explore the reactivity of carboxylic acids and esters, including hydrolysis, reesterification, and functional derivatives. Learn about saponification, soap formation, and applications of these compounds.

Reactive Chemistry of Carboxylic Acids and Esters
E N D
Presentation Transcript
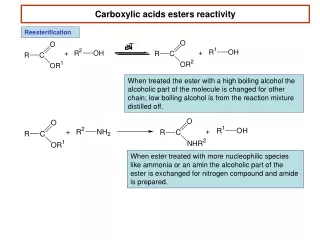
Carboxylic acids esters reactivity Reesterification When treated the ester with a high boiling alcohol the alcoholic part of the molecule is changed for other chain; low boiling alcohol is from the reaction mixture distilled off. When ester treated with more nucleophilic species like ammonia or an amin the alcoholic part of the ester is exchanged for nitrogen compound and amide is prepared.
Carboxylic acids esters reactivity Hydrolysis of esters acid catalysis basic catalysis (saponification) during base catalysed reaction salts of carboxylic acid are prepared the salts of long chain acids are caled soaps, (they are prepared by saponification of fats by NaOH and KOH) Ca2+ a Mg2+ salts are not soluble in water
Carboxylic acids esters reactivity Hydrolysis of fats by alcali - saponification mechanism of esters hydrolysis by alkalies after reaction are formed soaps and glycerol Application of soaps : lubricates, detergents
Carboxylic acids esters Fats (triglycerides) esters of fatty acids with glycerol nonsaturated acid have in living tissues always cis- configuration waxes
Infrared spektrum of esters nC=O = 1735-1750 cm-1
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids Reactivity: 1) Sensitivity of carbonyl to attack of a nucleophile is increased by electronwithrawing halogen Carboxylic acids halogenides Halogenide of acid …... Acyl halogenide acetylchloride acetic acid chloride benzoic acid chloride benzoyl chloride butyrylbromide butanoic acid bromide malondichloride malonic acid chloride cyclohexancarbonyl bromide
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids Acyl halogenides
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids esters amides anhydrides hydroxamic acids hydrazides MECHANISM azides
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids AMIDES maleinimide N-methyl- 3-nitrobenzamide acetamide ethanamide acetic acid amide ftalimide N,N-dimethylformamide formic acid N,N-dimethylamide succinimide pentanamide
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids • electron gap at carbonyl is smaller than that at esters and the reactions at amide are more difficult • hydrogen atoms at N-atom are acidic Compound
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids nN-H = 3200 – 3400 cm-1 nC=O = 1650 cm-1
Functional derivatives of carboxylic acids Hoffmann rearrangement nitrene isocyanate rearrangement carbamoic acid