Reproductive Anatomy Ch. 27
480 likes | 1.09k Vues
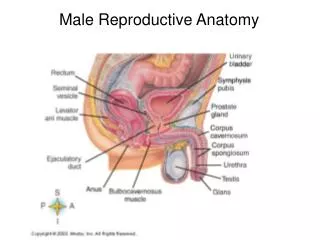
Reproductive Anatomy Ch. 27. Male Reproduction. The Testes. Each testis is surrounded by two tunics tunica vaginalis tunica albuginea Septa divide the testis into 250-300 lobules, each containing 1-4 seminiferous tubules Seminiferous tubules Produce sperm

Reproductive Anatomy Ch. 27
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Testes • Each testis is surrounded by two tunics • tunica vaginalis • tunica albuginea • Septa divide the testis into 250-300 lobules, each containing 1-4 seminiferous tubules • Seminiferous tubules • Produce sperm • Interstitial cells between tubules produce androgens • Tubulus rectus • Rete testis
After leaving the testes sperm go to • Efferent ductules • Epididymis • Ductus (vas) deferens • Site of vasectomy • Ejaculatory duct • and finally the Urethra
Male Reproductive System Figure 27.1
Scrotum • Sac of skin and superficial fascia • Hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis • Contains paired testicles separated by a midline septum • Keeps the testes ~3C lower than core body temperature • Position held by cremaster and dartos muscles
The Penis • Copulatory organ • Designed to deliver sperm into the female reproductive tract • Attached root and free shaft, ending in glans penis • Prepuce (foreskin) • Skin covering the distal end of the penis • Circumcision – surgical removal of the foreskin after birth
The Penis Figure 27.4
Internal penis • Part of the urethra • 3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue • spongy network of connective tissue, smooth muscle, and vascular spaces
Corpus spongiosum • surrounds urethra and expands to form the glans and bulb of the penis • Corpora cavernosa • paired dorsal erectile bodies
Accessory Glands Empty secretions into ducts that combine with sperm to form semen • Seminal vesicles • Prostate gland • Bulbourethral glands
1. Seminal Vesicles • Lie on the posterior wall of the bladder • Secretes 60% of the volume of semen • Join the ductus deferens to form the ejaculatory duct • Sperm and seminal fluid mix in the ejaculatory duct • Enter the prostatic urethra during ejaculation
Male Reproductive System Figure 27.1
2. Prostate Gland • Doughnut-shaped gland that encircles part of the urethra, inferior to the bladder • Accounts for 33% of the semen • Milky, slightly acid fluid • Contains citrate, various enzymes, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) • Plays a role in the activation of sperm • Enters the prostatic urethra during ejaculation
Male Reproductive System Figure 27.1
3. Bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands • Pea-sized glands inferior to the prostate • Produce thick, clear mucus prior to ejaculation
Male Reproductive System Figure 27.1
Semen • Provides a transport medium, nutrients, protection for and activates sperm • Viscous, alkaline fluid • Neutralizes the acid environment found in the male urethra and female vagina • Fructose + ascorbic acid provide nutrients for sperm • Prostaglandins • Decrease the viscosity of mucus in the cervix • Stimulates reverse peristalsis in the uterus • Relaxin hormone enhances sperm motility • Seminalplasmin acts as an antibiotic • Clotting factors + enzymes (vesiculase) coagulate semen immediately after ejaculation • Then fibrinolysin liquefies the sticky mass
Ejaculation • The propulsion of semen from the male duct system • At ejaculation, SNS cause: • Reproductive ducts and accessory organs to contract and empty their contents • The bladder sphincter muscle to constrict, preventing the expulsion of urine • Bulbospongiosus muscles to undergo a rapid series of contractions • Propulsion of semen from the urethra
Ovaries • Surrounded by • fibrous tunica albuginea • covered germinal epithelium
Female Reproductive Anatomy • Ovaries • Make female gametes (ova) • Secrete female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone) • Accessory ducts include uterine/fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina • External genitalia – external sex organs
The Ovaries Figure 27.14a
Ovaries • Follicles embedded in cortex • Each follicle consists of an immature oocyte • Cells around the oocyte are called: • Follicle cells • Granulosa cells
Ovaries • Primordial follicle – one layer of squamous-like follicle cells surrounds the oocyte
Ovaries • Primary follicle – two or more layers of cuboidal granulosa cells enclose the oocyte
Ovaries • Secondary follicle – fluid-filled space between granulosa cells that coalesces to form a central antrum
Ovaries • Graafian follicle – secondary follicle at its most mature stage that bulges from the surface of the ovary
Ovaries • Ovulation – ejection of the oocyte from the ripening follicle
Ovaries • Corpus luteum – ruptured follicle after ovulation
Uterine Tubes (Fallopian Tubes) and Oviducts • Receives ovulated oocyte • Site for fertilization • Oocyte moves into peritoneal cavity • Grasped by beating fimbriae of the infundibulum in the tube’s ampulla • Moves through tubes via peristalsis and ciliary action • Empties it into superolateral region of uterus, via the isthmus
Uterus • Hollow, thick-walled organ located in the pelvis anterior to the rectum and posterosuperior to the bladder • Body – major portion of the uterus • Fundus – rounded region superior to the entrance of the uterine tubes • Isthmus – narrowed region between the body and cervix • Cervix – narrow neck which projects into the vagina inferiorly
Uterine Wall • Composed of three layers • Perimetrium • outermost serous layer; the visceral peritoneum • Myometrium • middle layer; interlacing layers of smooth muscle • Endometrium • mucosal lining of the uterine cavity • glandular
Uterine Wall Figure 27.15b
Vagina • Thin-walled tube lying between the bladder and the rectum, extending from the cervix to the exterior of the body • The urethra is embedded in the anterior wall • Provides a passageway for birth, menstrual flow, and is the organ of copulation
External Genitalia: Vulva (Pudendum) • Lies external to the vagina and includes the mons pubis, labia, clitoris, and vestibular structures • Mons pubis – round, fatty area overlying the pubic symphysis • Labia majora – elongated, hair-covered, fatty skin folds homologous to the male scrotum • Labia minora – hair-free skin folds lying within the labia majora; homologous to the ventral penis
Vagina Figure 27.16
External Genitalia: Vulva (Pudendum) • Greater vestibular glands • Pea-size glands flanking the vagina • Homologous to the bulbourethral glands • Keep the vestibule moist and lubricated
External Genitalia: Vulva (Pudendum) • Clitoris (homologous to the penis) • Erectile tissue hooded by the prepuce • The exposed portion is called the glans • Perineum • Diamond-shaped region between the pubic arch and coccyx • Bordered by the ischial tuberosities laterally