Fish Internal Anatomy and Physiology
1.12k likes | 5.09k Vues
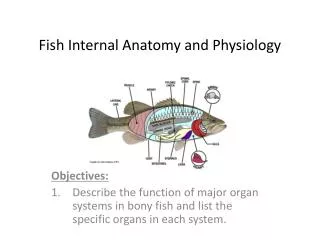
Fish Internal Anatomy and Physiology. Objectives: Describe the function of major organ systems in bony fish and list the specific organs in each system. Digestive System. food enters mouth through esophagus into the stomach for digestion

Fish Internal Anatomy and Physiology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fish Internal Anatomy and Physiology Objectives: Describe the function of major organ systems in bony fish and list the specific organs in each system.
Digestive System • food enters mouth through esophagus • into the stomach for digestion • Typically J-curvied, elongated, modified to grind, or lost • Intestine • Pyloric caecae – slender blind tubes that secrete digestive enzymes • liver secretes bile that breaks down fat
Digestive Continued • Carnivorous fishes • Short, straight intestines • Herbivorous fishes • Coiled intestine • Sharks • Spiral valve – increase surface area for digestion and absorbing nutrients
Circulatory System • two-chambered heart beneath the gills • gas exchange takes place in gills • oxygenated blood is carried through the arteries • Capillaries allow oxygen and nutrients to reach the cells • veins carry deoxygenated blood and carbon dioxide back to the heart
Irrigation of gills • “irrigate” – water flows over the gills • Cartilaginous fish • Open and close the mouth • Every gill is in its own chamber • 1st pair of gill slits is modified into spiracles • Allow bottom fish to breathe
Bony fish • Gills on each side share a gill chamber • When mouth opens, opercula close, pharynx expands, sucking in water • Lamellae • Thin plates in rows on gill filament • # of lamellae increase with active swimmers
Nervous System • central nervous system • brain and spinal cord • nerves connect the central nervous system with all of the organs • sensory organs • Eyes – focus moving closer and farther • Nictitating membrane – reduce brightness, protect during feeding • lateral lines – sense pressure changes, vibrations • nostrils and olfactory sacs – smell • taste buds – mouth, fins, skins, barbels • inner ears – hearing and balance
Special Organ • Swim bladder • Controls buoyancy • Inflates as the fish moves up • Deflates as it move deeper • Absorbs or releases gas into the bloodstream