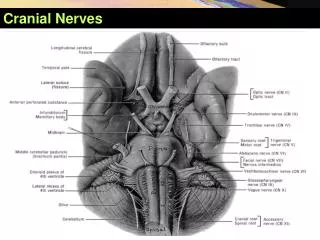
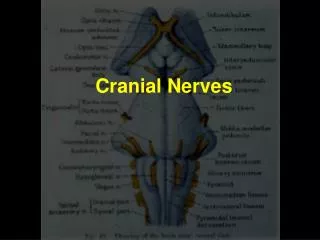
CRANIAL NERVES - LECTURE B
240 likes | 423 Vues
CRANIAL NERVES - LECTURE B. NBIO 401 – Friday, October 8, 2009. Abducens nucleus. Abducens nerve. Genu of the Facial nerve. Abducens nucleus. Facial nucleus. Facial nerve. Facial nerve fibers (looping around the abducens nucleus). Abducens Nucleus (eye muscle motoneurons).

CRANIAL NERVES - LECTURE B
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CRANIAL NERVES - LECTURE B NBIO 401 – Friday, October 8, 2009
Abducens nucleus Abducens nerve
Genu of the Facial nerve Abducens nucleus Facial nucleus Facial nerve
Facial nerve fibers (looping around the abducens nucleus) Abducens Nucleus (eye muscle motoneurons) Facial motor nucleus (muscles of facial expression) Facial motor nucleus
Solitary nucleus (outside) Abducens nucleus Superior salivatory nucleus Facial intermediate nerve part of facial nerve carrying: Motor motor output from the superior salivatory nucleus to some salivary glands (GVE) Sensory 1) taste information from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue to solitary nucleus via the solitary tract (SVA) 2) touch information from a small patch of skin on the ear and behind the ear to spinal trigeminal nucleus (GSA) Spinal trigeminal nucleus Facial intermediate nerve Solitary tract (inside)
Superior cerebellar peduncle Spinocerebellar fibers (on route to the cerebellum) Inferior cerebellar peduncle Middle cerebellar peduncle Superior cochlear nucleus Vestibulocochlear Nerve VIII Cochlear component (carries auditory signals from the cochlea to the cochlear nucleus)
Inferior vestibular nucleus Medial vestibular nucleus Vestibulocochlear Nerve VIII vestibular component (carries vestibular signals from the vestibular labyrinth to the vestibular nuclei) Inferior Cerebellar peduncle
Superior Cochlear nucleus Vestibulocochlear Nerve VIII Vestibular nuclei
Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract Inferior cerebellar peduncle (spinocerebellar fibers to cerebellum) Vestibular nuclei Hypoglossal Nucleus Solitary tract & nucleus MLF Cochlear Nucleus (auditory information) Spinothalamic Tract Medial lemniscus Inferior olive nucleus Pyramidal Tract Abducens nerve (to eye muscle) Pontine Gray matter (relay signals to cerebellum)
Inferior salivatory nucleus Solitary nucleus & tract Spinal trigeminal Nucleus Nucleus Ambiguus (motoneurons for larynx & pharynx muscles) Glossopharyngeal nerve IX carries: Motor signals to the pharynx from nucleus ambiguus motor output from the inferior salivatory nucleus to some salivary glands Sensory 1) taste information from posterior 1/3 of tongue to the solitary nucleus via the solitary tract. touch information from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, pharynx, some skin around the ear, internal surface of ear drum to the spinal trigeminal tract Pressure signals from the carotid artery
Dorsal motor nucleus of the Vagus Solitary nucleus & tract Nucleus ambiguus Spinal trigeminal nucleus Roots of the vagus nerve X carries: Motor motor signals to larynx & pharynx muscles from motoneurons in nucleus ambiguus. 2) parasympathetic output to the larynx & pharynx & to organs of the chest & abdomen from the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus Sensory touch signals from pharynx, external ear canal, external side of the ear drum, & skin of the ear to the spinal trigeminal nucleus. 2) taste information from the epiglottus to the solitary nucleus 3) sensory signals from the larynx, trachea, esophagus, chest & abdomen viscera, & pressure & chemoreceptors in the aorta to the caudal part of the solitary nucleus.
Nucleus Ambiguus (motoneurons for larynx & pharynx muscles) Lateral cuneate nucleus Vestibular nuclei Hypoglossal Nucleus (tongue motoneurons) Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract Solitary tract & nucleus DMX Spinocerebellar Tract MLF Spinothalamic Tract Medial lemniscus (touch information from body) Vagus Nerve Rootlet (motor commands to viscera in body) Pyramids Hypoglossal nerve (motor commands to tongue) Inferior olive nucleus (big input to cerebellum)
Spinal accessory nucleus (motoneurons for sternocleidomastoid & trapezius muscles) Spinal accessory nerve Spinal accessory roots
Gracile fasciculus Gracile Nucleus Cuneate nucleus Cuneate fasciculus Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract Spinal Accessory Nucleus MLF Pyramidal Decussation Spinothalamic Tract Pyramidal tract
Solitary nucleus & tract Vestibular nuclei Dorsal motor nuclei of the vagus External cuneate nucleus Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract Nucleus ambiguus Hypoglossal nuclei (motoneuron for tongue muscles) Inferior olive Hypoglossal nerve Pyramidal tract
Spinal trigeminal nucleus & tract Vestibular nuclei Hypoglossal Nucleus Solitary tract & nucleus Lateral cuneate nucleus DMX IVth ventricle Inferior olive Pyramidal tract Medial lemniscus
Somatic Motor Nuclei Oculomotor nucleus Hypoglossal nucleus Oculomotor nerve Trochlear nerve Hypoglossal nerve Trochlear nucleus Abducens nerve Abducens nucleus
Special visceral (Branchial) Motor Nuclei Trigeminal motor nucleus Trigeminal nerve Facial motor nerve Facial motor nucleus Nucleus ambiguus axons bound for glossopharyngeal & vagus nerves Nucleus ambiguus
General Visceral Motor Nuclei Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus Axons from the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus bound for the vagus nerve Inferior salivatory nucleus Superior salivatory nucleus Axons from the superior salivatory nucleus bound for the facial nerve Axons from the inferior salivatory nucleus bound for the glossopharyngeal nerve Edinger-Westphal nucleus Edinger-Westphal fibers bound for the oculomotor nerve
Somatic Sensory Nuclei Main sensory trigeminal nucleus Mesencephalic trigeminal tract Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus Trigeminal nerve (touch, conscious& unconscious proprioception, pain & temperature from the head to main sensory trigeminal nucleus, mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus & spinal trigeminal nucleus) Spinal trigeminal nerve Facial intermediate nerve (touch from ear to spinal trigeminal nucleus) Glossopharyngeal Nerve (touch from ear & pharynx to spinal trigeminal) Vagus nerve (touch from ear & pharynx to spinal trigeminal) Spinal trigeminal nucleus
Visceral Sensory Nuclei Facial intermediate Nerve (taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue to solitary nucleus) Glossopharyngeal nerve (taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue to solitary nucleus) Vagus nerve (taste from epiglottus to rostral solitary nucleus, signals from the trachea, esophagus, chest, abdomen & aorta to caudal part of solitary nucleus)