Cell Organelles
270 likes | 531 Vues
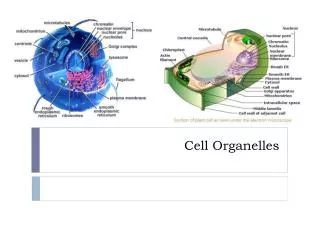
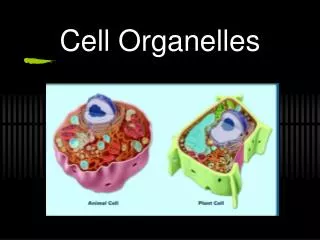
Cell Organelles. Honors Biology I. Cell Organelles. Organelle= “little organ”. Not found in Animal cells Support structure Made of cellulose Plasmodesmata allow materials to pass from one cell to the next. Cell Walls. Found only in animals Formed from protein tubulin

Cell Organelles
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cell Organelles Honors Biology I
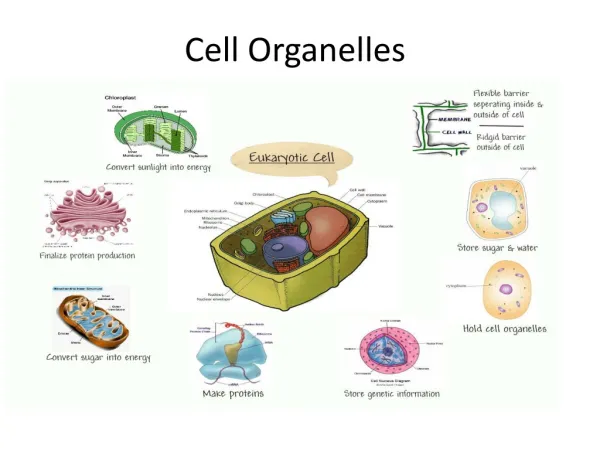
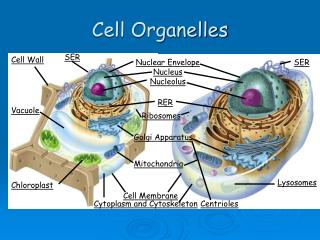
Cell Organelles • Organelle= “little organ”
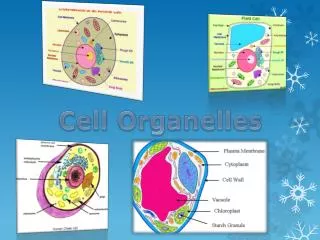
Not found in Animal cells Support structure Made of cellulose Plasmodesmata allow materials to pass from one cell to the next Cell Walls
Found only in animals Formed from protein tubulin Found near nucleus in the centrosome Help organize cell division Centrioles
“support and transport structure” Network of protein filaments 1. Microfilaments Thread-like Made of protein actin 2. Microtubules Hollow structures Made of protein tubulin Important during cell division when moving chromosomes Cytoskeleton
Plasma Membrane • We have already covered this!
Numerous hair-like extensions of the cell membrane Type of microtubule used for locomotion and aid in feeding Ex: respiratory cells Cilia
Long whip-like extensions of the cell membrane Type of microtubule Used for locomotion Ex: sperm cells Flagella
“control center” Contains DNA Nuclear envelope Composed of 2 membranes Contains nuclear pores that allow material to move in and out of nucleus Nucleus: Main Office
Chromatin DNA bound to protein Condenses into chromosomes during cell division Nucleolus Produces ribosomes Cells normally contain a single nucleus Cells such as liver and muscle cells have more than one due to amount of organelles that need controlling
Cytoplasm vs cytosol • All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol • Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm
“machines” Makes proteins Consists of ribosomal RNA and protein Free Ribosomes Found in the cytosol Make proteins for use in that cell Attached Ribosomes Attached to rough ER Make proteins to be transported elsewhere or to be inserted in the membrane Ribosomes
“conveyor belt” Consists of a series of membraneous tubules that connect to the nuclear envelope Rough ER has ribosomes and carries proteins throughout the cell Smooth ER does NOT have ribosomes and makes membrane lipids and detoxifies drugs Liver cells have large amounts of smooth ER Endoplasmic Reticulum
Vesicles • Transport organelles • Endocytosis and exocytosis • Protein transport
“mail room” Stack of membraneous sacks Receives proteins from the Rough ER and then modifies, sorts and packages them in vesicles for storage or transport Golgi Apparatus
“storage” Sac-like membrane bound structures Store water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates etc. Plant cells have a large central Vacuole Pressure inside offers support to plant structures Animal cells have smaller vacuoles Vacuoles
“solar power” Only found in Plant cells Double membrane Site where photosynthesis takes place Contains chlorophyll pigment that absorbs light Have their own DNA Chloroplasts
“Powerhouse” Double membrane organelle outer membrane Inner membrane: contains folds called Cristae which increases surface area for cellular respiration to take place Convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that the cell can use Mitochondria
Inherited from your mom Contain their own DNA Numerous in muscle cells
“clean up crew” Small organelles filled with enzymes Digests lipids, carbohydrates and proteins so that they can be used by the cell Get rid of “worn-out” organelles Lysosomes
Lynn Margulis suggested that mitochodria and chloroplasts are descendants of prokaryotes Large prokaryotes consumed smaller prokaryote which developed a symbiotic relationship Evolution of first eukaryote Endosymbiotic Theory