Lipids
590 likes | 886 Vues
Lipids. Prof.Dr .Gülden Burçak 2011-2012. Heterogenous group Insoluble in water , soluble in nonpolar solvents Dietary constituents Adipose tissue Myelinated nerves Lipoproteins Obesity , diabetes mellitus , atherosclerosis. 1) Simple lipids Fats Waxes 2) Complex lipids

Lipids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lipids Prof.Dr.Gülden Burçak 2011-2012
Heterogenousgroup • Insoluble in water, soluble in nonpolarsolvents • Dietaryconstituents • Adiposetissue • Myelinatednerves • Lipoproteins • Obesity, diabetesmellitus, atherosclerosis
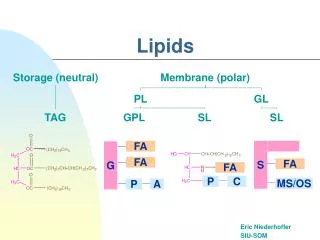
1)Simplelipids Fats Waxes 2)Complexlipids Phospholipids Glycolipids (glycosphingolipids) Sulfolipids,aminolipids,lipoproteins 3)Precursorandderivedlipids Fattyacids, glycerol, steroids, other alcohols, fattyaldehydes, ketonebodies, hydrocarbons, lipid-solublevitamins, hormones
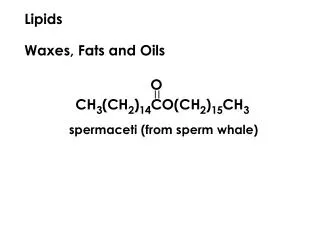
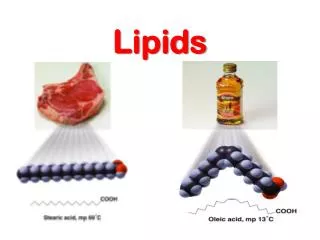
Simple lipids • Fats : Esters of fattyacidswithglycerol A fat in theliquidstate : oil • Waxes :Esters of fattyacidswithhighermolecularweightmonohydricalcohols
Unchargedlipidsarecalledneutrallipids • Acylglycerols • Cholesterol • Cholesterylesters
Fatty acids • Esterified and unesterified • Even numbered, straight-chain derivatives • Saturated and unsaturated
Nomenclature • -oic, -anoic, -enoic • Numberedfromthecarboxylcarbon (carbon no 1) • α, ß, γ……………..ω ( terminal CH3carbon) • ∆ : numberandposition of doublebonds • ∆9 :doublebondbetween C 9 and C10 • ω9:doublebond on C 9 countingfromtheωC ; ω9, ω6, ω3
Unsaturated fatty acids • 1)Monounsaturated • 2)Polyunsaturated • 3)Eicosanoids • derivedfromeicosa (20C) polyenoicfattyacids : prostanoids,leukotrienesandlipoxins
Essential fatty acids • Linoleicacid (ω-6) • α-Linolenicacid (ω-3) • Arachidonicacid (ω-6) can be formedfromlinoleicacid.
Naturallyoccuringunsaturatedfattyacids • arenearlyall of cisconfiguration • L-shaped • A highnumber of cisdoublebondsleadsto a variety of possiblespatialconfigurations • Arachidonicacidwithfourcisdoublebonds has kinksor U shape • Spatialrelationships in plasmamembranephospholipidsareimportant • Trans fattyacidsdisturbthespatialrelationships
Melting point • Chain length • Degree of unsaturation • Membrane lipids are more unsaturated than storage lipids.
Eicosanoids • Parentcompound :C20polyunsaturatedfattyacids • Physiologicallyandpharmacologicallyactivecompounds • Prostanoids • prostaglandins (PGs) • prostacyclins (PGIs) • thromboxanes (TXs) • Leukotrienes (LTs) • Lipoxins (LXs)
Prostaglandinscausecontraction of smoothmusclecells • Prostacyclinsarepotentinhibitors of plateletaggregation • Thromboxanescausevasoconstrictionandplateletaggregation • Leukotrienesandlipoxinsarepotentregulators of manydiseaseprocesses • Leukotrienesarepotentproinflammatoryagents
Prostaglandin E2 Thromboxane A2 LeukotrieneA4
Triacylglycerols : Storage Mixed triacylglycerol 1,3-Distearopalmitin
Phospholipids 1) Phosphatidicacidandphosphatidylglycerol 2) Phosphatidylcholine 3) Phosphatidylethanolamine 4) Phosphatidylinositol 5) Phosphatidylserine 6) Lysophospholipids 7) Plasmalogens 8)Sphingomyelins
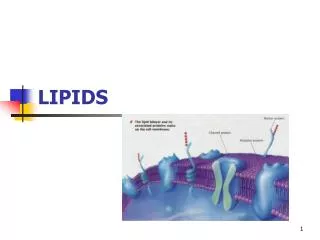
Phosphatidylcholines • Mostabundant in theplasmamembrane • Saturatedacylradical in C1positionandunsaturated in the C2 • Choline: hepaticlipoproteinsynthesisandexport ; acetylcholine
Dipalmitoyllecithin • Surface-activeagent (surfactant) in thelung • Alveolarwallsare not strongenoughtomaintaintheirshapeagainstthesurfacetension of water. • Dipalmitoyllecithinandsphingomyelinssecretedtothelungchamberpreventtheadherence of theinnersurfaces of thealveoli • Respiratorydistresssyndrome
Phosphatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate : a precursor of second messengers
Diphosphatidylglycerol (Cardiolipin) Mitochondrial membranes
Lysolecithin • Lysophospholipids : important in the metabolism and interconversion of phosholipids. • Phospholipase A2 : formation of a lysophospholipid
Plasmalogens • Brain and muscle tissue
Sphingomyelins • Brainandnervetissue
Glycolipids • In cell surface carbohydrates • Particularly in the nervous tissue • Glycosphingolipids • Galactosylceramide : neural tissues • Glucosylceramide : extraneural tissues
Galactosylceramide (Galactocerebroside) • Brainandothernervoustissue • C24 : lignoceric, cerebronic , nervonic , oxynervonicacids • Sulfogalactosylceramide (sulfatide) : myelin
Gangliosides • Complex glycosphingolipids • Glucosylceramide + one or more sialic acids • Nervous tissue
Sialic acid : N-acetyl neuraminic acid Neuraminicacid : 9Csugarderivedfrommannosamineandpyruvate
Steroids • Thesterane ring Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene, a tetracyclichydrocarbon • Steroidnucleus
Cholesterol • Widely distributed in all cells,particularly in the nervous tissue • Plasma membrane and lipoproteins • In animal fats • Reduction of double bond : coprostanol (coprosterol)
Ergosterol A precursor of vitamin D
Isopreneandpolyprenoids : dolichol, ubiquinone C95 alcohol
Plant derived isoprenoids • Fatsolublevitamins • Vitamin A • Vitamin D • Vitamin E • Vitamin K