Lipids
220 likes | 804 Vues
Lipids. Aims. Elements of lipids Structure of glycerol & fatty acids Condensation reactions to form triglycerides Phospholipids. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vccnaNSwUs4. What does this have to do with lipids? How does the hump help the camel survive?

Lipids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Aims • Elements of lipids • Structure of glycerol & fatty acids • Condensation reactions to form triglycerides • Phospholipids
What does this have to do with lipids? How does the hump help the camel survive? What is the related biochemical reaction?
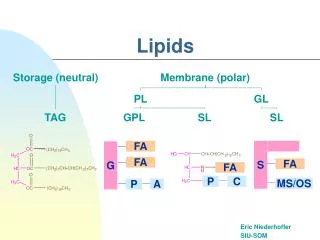
Introduction to lipids • Lipids contain the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. • They have numerous functions, primarily energy stores in animals and plants. • Lipids consist of two types of molecules - glycerol & fatty acids.
Glycerol • A molecule of glycerol is made up of three carbon atoms. • Each of these has a hydroxyl group attached to it. • Hydrogen atoms occupy the remaining positions.
Fatty Acids • A single fatty acid molecule contains an acid (COOH) group attached to a hydrocarbon chain. • Hydrocarbon usually denoted by the letter ’R’. • Saturated = If every carbon atom in the chain is joined by a single C-C bond. • Unsaturated = at least one C=C bond. • Polyunsaturated = many double bonds. • Most animal fats are saturated while most plant fats are unsaturated.
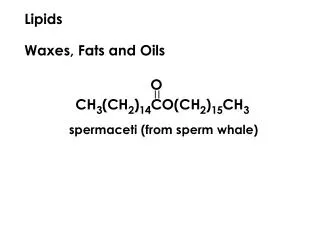
Triglycerides • A triglyceride molecule is made of a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids. • The molecules join together through the process of condensation losing a molecule of water each time a link is made. • The link between the glycerol molecule & each fatty acid is an ‘Ester Link’. • The fatty acids in a lipid molecule can differ in length and can be saturated or unsaturated.
Phospholipids • In phospholipids one of the fatty acids of a triglyceride is substituted by a phosphate group.
Lipids & water • Triglycerides and phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups. • What does this mean? • To what use is this feature put in biology? • What happens when you mix oil in water? Describe and explain.
Makes notes on cholesterol and steroids • Draw and compare them (find the relevant challenge question on the challenge board in S8)
More Info • To make further notes on Lipids : • www.mrothery.co.uk • www.biologymad.com • http://chemincontext.eppg.com/chapter11/cic_interface11.swf • http://www.cassiopeiaproject.com/videos.php